
Version 1.3.1 ⤵️
Last Updated: February 2026
FREE DOWNLOAD
Table of Contents
Introduction
What is WP Optimal State?
 WP Optimal State is a comprehensive database optimization and maintenance plugin designed to keep your WordPress website running at peak performance. Over time, WordPress databases accumulate unnecessary data such as post revisions, spam comments, orphaned metadata, and expired transients. This bloat can slow down your site and increase hosting costs.
WP Optimal State is a comprehensive database optimization and maintenance plugin designed to keep your WordPress website running at peak performance. Over time, WordPress databases accumulate unnecessary data such as post revisions, spam comments, orphaned metadata, and expired transients. This bloat can slow down your site and increase hosting costs.
WP Optimal State provides an intuitive interface to safely identify, review, and remove this unnecessary data while optimizing your database tables for maximum efficiency. Key features include one-click optimization, detailed cleanup options, advanced table optimization and repair, an integrated database backup and restore manager with enhanced safety features, a database health score, database structure analysis, an automated cleaning scheduler with email notifications, and a performance features manager to enable or disable WordPress core functions.
The plugin offers a range of performance-enhancing features in the fine-tuning section to speed up your site’s loading time. These include a dual caching system that relies upon both the server and the browser, along with the ability to remove unused WordPress components.
Essentially, WP Optimal State Pro is five plugins in one:
- Database Cleanup and Optimization
- Database Backup and Restore
- Database Search & Replace
- Caching and Performance Tuning
- Brute Force Protection
It can easily replace the following plugins, saving you a considerable amount of money:
UpdraftPlus, WP Database Backup, WP Rocket, WP Super Cache, WP-Optimize, Better Search Replace, Heartbeat Control, Perfmatters, WP Revisions Control, Clearfy, Advanced Database Cleaner, Autoptimize, Loginizer.
⚠️ Compatibility Notice: This plugin is designed for single-site WordPress installations only. It is not compatible with WordPress Multisite networks.
Key Benefits
- Improved Performance: Reduce database size and query times
- Better User Experience: Faster page loads and admin operations
- Cost Savings: Smaller databases mean lower hosting costs
- Easy Maintenance: One-click optimization for routine cleaning
- Automated Scheduling: Set-it-and-forget-it database maintenance
- Full Control: Choose exactly what to clean and when
- Safe Operations: Clear warnings for potentially destructive actions
- Advanced Table Management: Analyze and repair tables with enhanced diagnostics
- Integrated Backups: Create, manage, and safely restore database backups
- Health Monitoring: Understand database condition with a health score
- Structure Insights: Analyze core vs. plugin tables
- Core Feature Control: Disable unused WP features (Heartbeat, XML-RPC, etc.)
Who Should Use This Plugin?
- Website Owners: Keep your site fast and efficient
- Developers: Maintain clean development and staging environments
- Agencies: Regular maintenance for client websites
- Bloggers: Manage post revisions and comment spam
- E-commerce Sites: Optimize product databases and transients
- Performance Enthusiasts: Fine-tune WordPress core features
Free Version vs Pro Version
The free version of WP Optimal State has some limitations compared to the pro version, but these limitations do not affect its usability. The free version is still perfectly functional and powerful. Check out a detailed comparison of free and pro versions below:
| Feature | Free Version | Pro Version |
|---|---|---|
| 🗄️ Database Backup & Restore | ||
| Create Database Backups | ✓ Yes | ✓ Yes |
| Maximum Backups to Keep | 1 | Up to 10 |
| Download Backups | ✓ Yes | ✓ Yes |
| Restore from Existing Backups | ✓ Yes | ✓ Yes |
| Restore Database from Uploaded File | ✓ Yes (50MB) | ✓ Yes (5GB) |
| Backup Verification (Checksum) | ✓ Yes | ✓ Yes |
| 🧹 Database Cleanup & Optimization | ||
| One-Click Optimization | ✓ Yes | ✓ Yes |
| Database Health Score | ✓ Yes | ✓ Yes |
| Database Statistics | ✓ Yes | ✓ Yes |
| Detailed Database Cleanup (18 cleanup types) | ✓ Yes | ✓ Yes |
| Optimize All Tables | ✓ Yes | ✓ Yes |
| Analyze & Repair Tables | ✗ No | ✓ Yes |
| Optimize Autoloaded Options | ✗ No | ✓ Yes |
| Database Structure Analysis | ✓ Yes | ✓ Yes |
| MySQL Index Manager | ✗ No | ✓ Yes |
| Referential Integrity Scanner | ✓ Yes | ✓ Yes |
| Database Search & Replace | ✗ No | ✓ Yes |
| Delete Unused Tables | ✗ No | ✓ Yes |
| Legacy Plugin Data Scanner | ✓ Yes | ✓ Yes |
| ⏰ Automation Features | ||
| Automatic Backup and Cleaning (Scheduled Tasks) | ✗ No | ✓ Yes |
| Email Notifications for Scheduled Tasks | ✗ No | ✓ Yes |
| Customizable Schedule (Every X Days at Specific Time) | ✗ No | ✓ Yes |
| 🚀 Performance Features | ||
| Server-Side Page Caching | ✓ Yes | ✓ Yes |
| Browser Caching (.htaccess Rules) | ✓ Yes | ✓ Yes |
| Cache Purging | ✓ Yes | ✓ Yes |
| Cache Statistics | ✓ Yes | ✓ Yes |
| Automatic Cache Preload (Sitemap-Based) | ✗ No | ✓ Yes |
| Mobile-Specific Cache | ✗ No | ✓ Yes |
| Custom Consent Cookie Support | ✗ No | ✓ Yes |
| Query String Handling Modes (3 Options) | ✓ Yes | ✓ Yes |
| Smart Cache Invalidation on Content Updates | ✓ Yes | ✓ Yes |
| Database Query Caching | ✗ No | ✓ Yes |
| Font Loading Optimization | ✗ No | ✓ Yes |
| Lazy Load Images & Iframes | ✓ Yes | ✓ Yes |
| Bad Bot Blocker | ✓ Yes | ✓ Yes |
| Post Revisions Limit Control | ✓ Yes | ✓ Yes |
| Trash Auto-Empty Control | ✓ Yes | ✓ Yes |
| Heartbeat API Control | ✓ Yes | ✓ Yes |
| Disable XML-RPC | ✓ Yes | ✓ Yes |
| Remove Emoji Scripts | ✓ Yes | ✓ Yes |
| Remove Unused WordPress Headers | ✓ Yes | ✓ Yes |
| Integrated PageSpeed Metrics | ✓ Yes | ✓ Yes |
| 🔒 Security & Safety | ||
| Automatic Safety Backup Before Restore | ✓ Yes | ✓ Yes |
| Emergency Rollback on Restore Failure | ✓ Yes | ✓ Yes |
| Temporary Table Swap (Zero-Downtime Restore) | ✓ Yes | ✓ Yes |
| Database Validation Before Restore | ✓ Yes | ✓ Yes |
| Maintenance Mode During Restore | ✓ Yes | ✓ Yes |
| Protected Backup Directory (.htaccess) | ✓ Yes | ✓ Yes |
| User Management (Restrict Access) | ✗ No | ✓ Yes |
| Settings Export & Import | ✓ Yes | ✓ Yes |
| Brute Force Protection | ✓ Yes | ✓ Yes |
| 📊 Logging & Monitoring | ||
| Optimization History Log (Last 80 Operations) | ✓ Yes | ✓ Yes |
| Detailed Operation Results | ✓ Yes | ✓ Yes |
| Real-Time Progress Tracking | ✓ Yes | ✓ Yes |
| 💬 Support & Documentation | ||
| Comprehensive Plugin Manual | ✓ Yes | ✓ Yes |
| Multi-Language Interface Support | ✓ Yes | ✓ Yes |
| In-Dashboard Help & Tooltips | ✓ Yes | ✓ Yes |
| Price | ✓ FREE | $105 Lifetime ✓ Terms & Conditions |
| Summary | Core Features | All Features |
Installation
Manual Installation
- Download the plugin ZIP file
- Log in to your WordPress admin dashboard
- Navigate to Plugins → Add New
- Click Upload Plugin at the top
- Click Choose File and select the ZIP file
- Click Install Now
- Click Activate Plugin when installation completes
- Look for “Optimal State” in your admin menu
Installation via FTP
- Download and extract the plugin ZIP file
- Upload the extracted plugin folder (named `optistate`) to
/wp-content/plugins/ - Log in to your WordPress admin dashboard
- Navigate to Plugins
- Find “WP Optimal State” and click Activate
- Look for “Optimal State” in your admin menu
Automatic Installation
- Log in to your WordPress admin dashboard
- Navigate to Plugins → Add New
- Search for “Optimal State”
- Click Install Now next to the plugin
- Click Activate when installation completes
- Look for “Optimal State” in your admin menu
System Requirements
- WordPress: 5.5 or higher
- WordPress Installation Type: Single-site only (Multisite not supported)
- PHP: 7.4 or higher
- MySQL: 5.6 or higher (or MariaDB 10.0+)
- User Permission: Administrator access required
- File System: Writable `wp-content/uploads/` directory for backups, settings, and logs.
Getting Started
First-Time Setup
Step 1: Access the Plugin
After activation, you’ll find Optimal State in your WordPress admin menu with a performance icon ![]() .
.
Click on Optimal State to access the main dashboard.
Step 2: Create a Database Backup
⚠️ CRITICAL STEP – DO NOT SKIP!
Before using any cleanup features:
- Navigate to section 1. Create a Database Backup
- Click Create Backup Now button
- Wait for the backup process to complete.
- Optional but Recommended: Download the newly created database backup file to your local device for extra safety.
Additional Backup Methods:
- Use your hosting control panel’s backup feature
- Use a dedicated backup plugin (UpdraftPlus, BackupBuddy, etc.)
- Use phpMyAdmin to export your database
- Contact your hosting provider for backup assistance
Step 3: Review Statistics
The plugin will automatically scan your database upon loading and display statistics about various data types like:
- Post revisions count
- Auto drafts
- Trashed items
- Spam comments
- Orphaned metadata
- Transients
- Database size and overhead
Take a moment to review these numbers to understand your database health. You can refresh these stats using the “Refresh Stats” button.
Step 4: Start with Safe Operations
For your first cleanup, we recommend using the One-Click Optimization feature (Section 2). This performs multiple safe cleanup operations and optimizes tables, providing a good initial boost without affecting your published content.
Dashboard Overview
Main Interface Sections
1. & 1.1. Database Backup and Restore
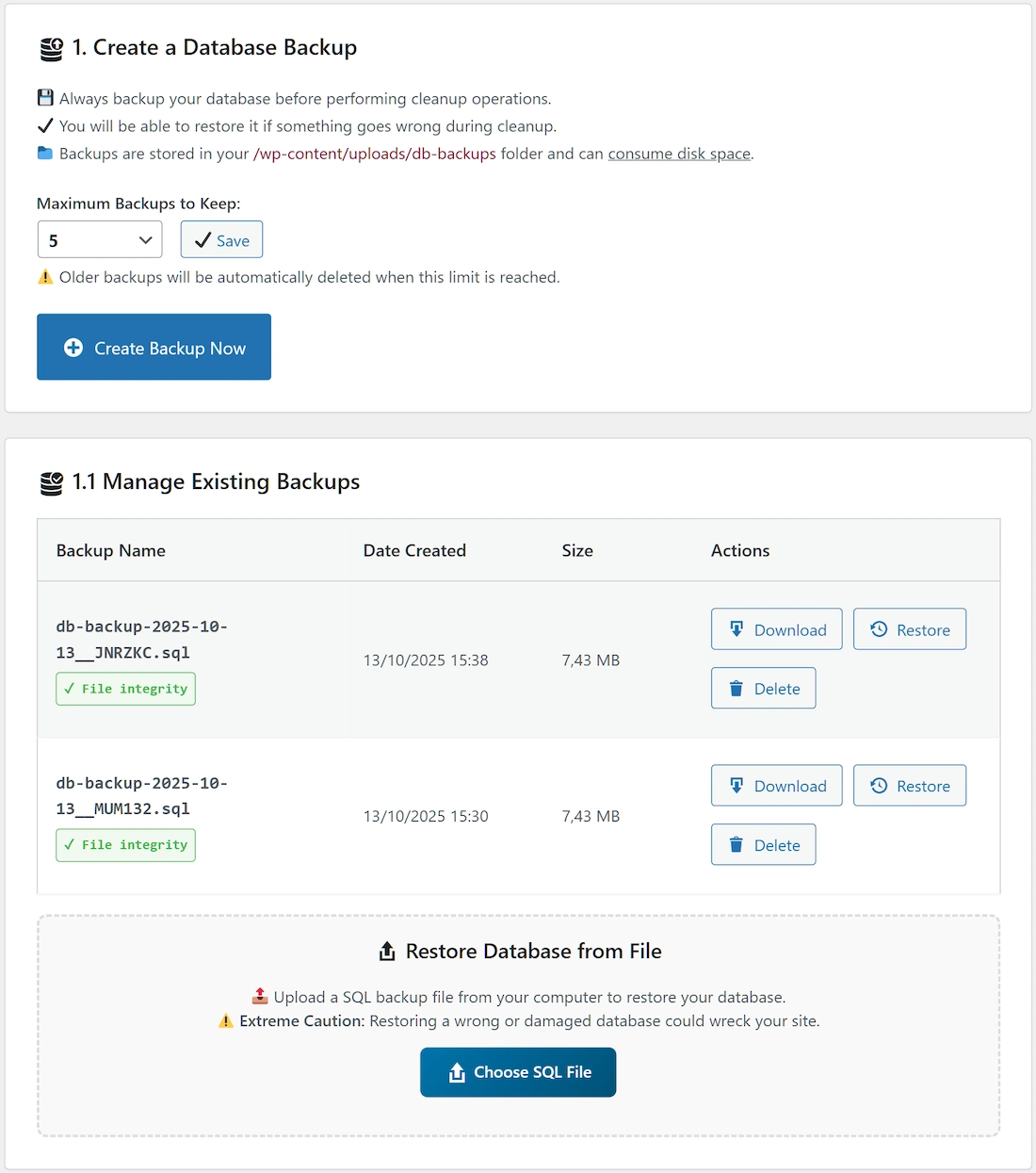
This section provides all the necessary tools to manage the safety state of your WordPress database before and after performing optimization tasks. It is highly recommended to use the backup feature before any cleanup operation.
Maximum Backups to Keep
This option allows you to customize the maximum number of backups to be stored.
- Allowed range: between 1 and 10
- Default value: 3
When the maximum limit is reached, oldest backups are automatically deleted. Click the “Save” button next to the dropdown to apply changes.
Create Backup Now
This button initiates an immediate, on-demand backup of your entire WordPress database. The generated `.sql.gz` file is added to the list below.
The backup files for your website are automatically saved to the following directory within your hosting account:
/wp-content/uploads/optistate/db-backups/. This directory is protected against direct web access.
⚠️ WARNING: If your server runs on Nginx, directory protection will not be set automatically (you need to configure it manually).
File Integrity Verification System
The plugin includes an advanced file integrity verification system that automatically validates every backup using SHA-256 checksums:
- ✓ File integrity – Backup file has been verified (checksum matched) and is likely not corrupted.
- ⚠ File integrity – Backup file verification failed (checksum mismatch) or metadata is missing. The file may be corrupted or incomplete.
Each backup includes verification data:
- SHA-256 Checksum (`.checksum` file) – Ensures file integrity against corruption or tampering.
- Metadata (`.meta` file) – Stores information like creation date, size, and WordPress version for validation.
- Automatic Verification – Files are automatically checked for integrity before restore operations.
Security Features:
- Backup directory is protected with .htaccess restrictions and an index.php file.
- All backup files include verification data (.checksum and .meta files).
- Automatic corruption detection prevents restoring damaged backups.
- Downloads are only allowed after nonce and permission checks.
- File integrity is verified before download streaming begins.
Download
Located next to each backup entry in the list, this action allows you to download the specific backup file to your local device for safekeeping (it will download as compressed .sql.gz file). The file’s integrity is verified before the download starts.
Restore
Use this button to revert your entire database to the state recorded in the corresponding backup file. This action is irreversible and requires a final confirmation in a modal window. The plugin performs integrity checks and creates a temporary “safety backup” before proceeding. See the detailed restore process explanation below. Use with prudence.
Restore Database from File
This feature allows you to restore your WordPress database by uploading a `.sql` or `.sql.gz` backup file from your computer (max 5GB).
- It performs security checks on the uploaded file (size, type, content).
- It includes basic validation to ensure the file looks like a WordPress database backup (checks for core tables and database name).
- While primarily designed for backups created by WP Optimal State, it may work with standard SQL files exported from tools like phpMyAdmin if they meet the validation criteria, but compatibility is not guaranteed.
- It uses the same safe restore process (safety backup, temporary tables, atomic swap) as restoring listed backups.
⚠️ Use Extreme Caution: Restoring a wrong or damaged database could wreck your site. Always ensure the backup is correct for the site you are restoring to.
How Database Restore Works — and Ensures Data Integrity
When you restore a database backup in WP Optimal State (either from the list or an uploaded file), the plugin executes a sophisticated, multi-stage process engineered for zero-risk data integrity. It goes far beyond a simple import, employing a transactional “atomic swap” system that ensures your site is never left in a broken or partially restored state. The process is built on four distinct phases, with comprehensive safety nets at every step.
Phase 1: Preemptive Safety Backup & Integrity Verification
Before the restore process begins, critical pre-checks are performed:
- Integrity Verification: For listed backups, the plugin calculates the SHA-256 checksum of the backup file and compares it against the securely stored .checksum file. If they don’t match, or if metadata is missing/invalid, the operation is aborted. For uploaded files, structural validation and security scans are performed.
- Safety Backup Creation: Once the backup file passes verification, the plugin creates a complete, real-time backup of your current database (named SAFETY-RESTORE-…). This “safety backup” acts as an immediate rollback point, preserving the exact state of your site before the restore began. If this safety backup fails, the restore is aborted.
Maintenance Mode: The plugin activates a maintenance mode for non-admin users during the critical restore phases to prevent data inconsistencies.
Phase 2: Isolated & Chunked Staging in Temporary Tables
Instead of directly overwriting your live tables—a risky operation that could lead to data corruption if interrupted—the plugin restores the backup data in isolation. To handle large files without server timeouts, the plugin divides the import into small, timed chunks. It processes a portion of the .sql file, then pauses and starts a new request to continue where it left off. In each chunk, it reads the SQL commands and executes them, but with all table names rewritten to use a temporary prefix (e.g., optistate_temp_wp_posts). This chunking process continues until the entire file is imported. During this entire phase, your live website remains active (though visitors see a maintenance page), running on the original, untouched database tables.
Phase 3: Post-Restore Data Verification
Once the final chunk has been imported into the temporary tables, the plugin performs a crucial verification step. It checks the newly created temporary tables to ensure that essential WordPress core tables (like optistate_temp_wp_options, optistate_temp_wp_users, and optistate_temp_wp_posts) exist, contain data, and include critical values (like the siteurl option). This sanity check confirms the backup was not empty or critically flawed. If this verification fails, the process is aborted, temporary tables are cleaned up, and the system proceeds directly to the automatic rollback procedure using the safety backup.
Phase 4: The Atomic Swap Transaction
This is the core of the safety mechanism. Only after the backup file has been staged and verified does the plugin interact with the live database. It performs the switch using a single, atomic database transaction. Inside this transaction, a series of RENAME TABLE commands are executed almost instantly:
- The live wp_posts table is renamed to optistate_old_wp_posts.
- The temporary optistate_temp_wp_posts table is renamed to wp_posts.
This sequence repeats for every table included in the backup. Because these commands are wrapped in a transaction, they are treated as a single, all-or-nothing operation. It’s impossible for only some tables to be swapped. The transaction either completes entirely (COMMIT), or it fails completely, and the database engine automatically reverts all renames within that transaction.
The Unbreakable Rollback Guarantee
This multi-phase architecture provides layers of protection:
- Automatic Async Rollback: If any critical error occurs during Phase 2 (Staging), Phase 3 (Verification), or Phase 4 (Swap Transaction), the plugin immediately halts, cleans up temporary tables, and triggers an asynchronous rollback. This special rollback runs in a separate, fresh process to ensure it has the time and resources to complete, automatically restoring the “Safety Backup” created in Phase 1.
- Transactional Safety: The atomic swap (Phase 4) itself is protected by the database transaction. If the transaction fails mid-swap, the database engine rolls back the renames within that transaction. The plugin then also triggers the asynchronous safety backup restore.
- Emergency Failsafe: The process includes multiple safeguards against fatal PHP errors or server crashes. A general shutdown function deactivates maintenance mode, while a second, specialized shutdown function monitors the (Phase 4) atomic swap, forcing a database
ROLLBACKif the script dies unexpectedly during that critical step. Maintenance mode is also deactivated in such cases.
Post-Restore Actions:
- If the swap is successful, the temporary “old” tables (optistate_old_…) are dropped.
- The safety backup file is deleted.
- WordPress object cache is flushed.
- Maintenance mode is deactivated.
- Relevant transients (stats, health score) are cleared.
This robust system ensures that a database restore is not a gamble—it either succeeds completely or it fails safely, with mechanisms in place to automatically revert to the original data.
2. & 3. One-Click Optimization + Database Health Score

2. One-Click Optimization (Blue gradient button with rocket icon 🚀)
Performs a bundle of safe cleanup operations and optimizes all database tables with a single click.
Comprehensive Cleanup Operations Included:
- Post Revisions
- Auto Drafts
- Trashed Posts
- Spam Comments
- Trashed Comments
- Orphaned Post Metadata
- Orphaned Comment Metadata
- Orphaned Relationships
- Expired Transients
- Duplicate Post Metadata
- Duplicate Comment Metadata
- Orphaned User Metadata
- Pingbacks
- Trackbacks
- Database Table Optimization (Runs `OPTIMIZE TABLE` on all tables)
When to Use One-Click Optimization:
- Weekly Maintenance: Recommended for regular upkeep.
- After Major Content Updates
- When Site Feels Sluggish
- Before Important Events
- After Plugin/Theme Changes
- When Health Score is below optimal
Safety Features:
- Operations primarily target unnecessary or already deleted data.
- No impact on published content or active users.
- Detailed log of actions performed is usually available via results display.
- Operations are permanent but can be reverted by restoring a database backup created beforehand.
Note: It’s always recommended to create a database backup before performing optimization operations.
3. Database Health Score Overview
The Database Health Score provides an assessment (0-100 points) of your database’s condition based on cleanliness, performance, and efficiency metrics derived from the database statistics.
It evaluates factors like:
- Database table overhead (fragmentation)
- Size of autoloaded options
- Accumulated unnecessary data (revisions, drafts, spam, orphans, etc.)
- Total database size
- Total number of tables
- Ratio of index size to total size
Score Interpretation:
- 90-100 (Excellent): Database is highly optimized.
- 70-89 (Good): Generally healthy, minor optimizations possible.
- 50-69 (Fair): Some clutter or inefficiency present; optimization recommended.
- 30-49 (Poor): Significant clutter or performance issues likely; optimization strongly recommended.
- 0-29 (Critical): Major issues detected; immediate optimization and investigation needed.
Components:
- Overall Score: Weighted average of the categories.
- Category Scores: Performance, Cleanliness, Efficiency.
- Recommendations: Specific actions suggested based on identified issues (e.g., “High table overhead detected”, “Excessive post revisions found”).
- Refresh Button: Allows recalculating the score after performing optimizations or if stats seem outdated.
4. Database Statistics Panel
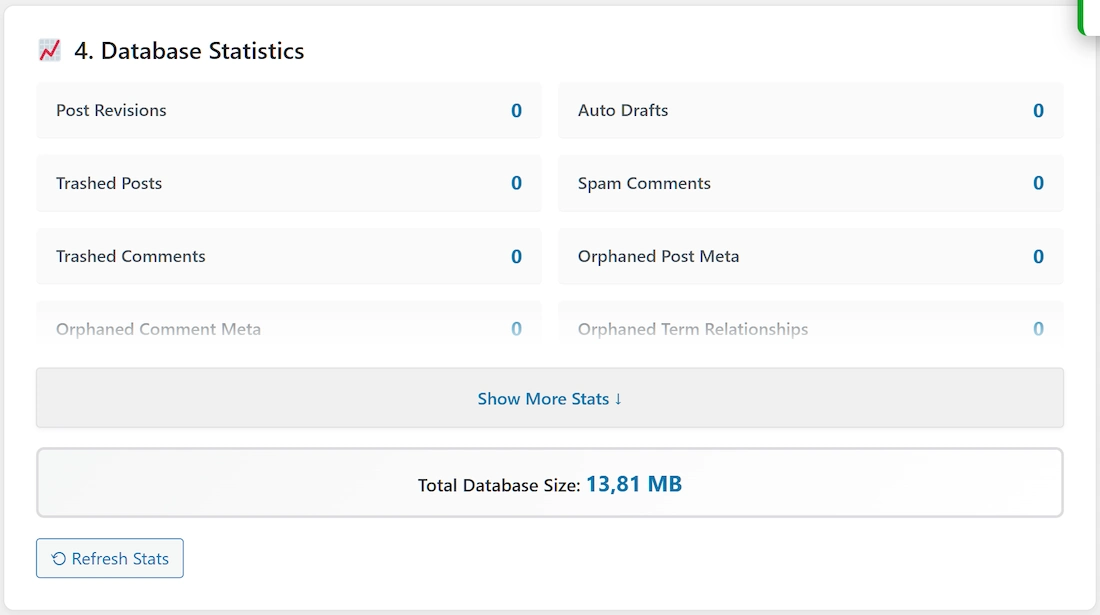
White card with chart icon 📊
Displays real-time (cached for 30 minutes unless refreshed) statistics about your database elements relevant to optimization:
- Post Revisions
- Auto Drafts
- Trashed Posts
- Spam Comments
- Trashed Comments
- Orphaned Post Meta
- Orphaned Comment Meta
- Orphaned Relationships (Term relationships for deleted objects)
- Expired Transients
- All Transients
- Orphaned User Meta
- Unapproved Comments
- Pingbacks
- Trackbacks
- Database Overhead (Estimated reclaimable space in tables)
- Total Indexes Size
- Autoloaded Options Count
- Autoloaded Options Size
- Total Tables Count
- Database Creation Date (Based on the first post’s date)
- Total Database Size (Calculated via separate AJAX call)
Show More/Less Button: Expands or collapses the list if there are many statistics.
Refresh Stats Button: Click to manually clear the cache and fetch fresh statistics.
5. Database Cleanup Section

Grid of individual cleanup items 🧹
Allows you to run specific cleanup tasks individually. Each item shows:
- Title: Type of data (e.g., “Post Revisions”)
- Count: Number of items found (badge). Displayed if count > 0.
- Description: Explanation of the data type.
- Warning Icon ⚠️: Appears next to operations that permanently delete potentially recoverable data (like Trashed Posts, Unapproved Comments, All Transients). Hover for tooltip.
- Clean Now Button: Initiates cleanup for that specific item. Disabled if count is 0. Shows loading state during operation.
6. Advanced Database Optimization Section

Tools for table-level optimization and analysis 🗄️
Three main functions and one analysis tool:
Optimize All Tables
- Runs `OPTIMIZE TABLE` on all database tables.
- Reclaims unused space (overhead).
- Defragments tables and updates index statistics.
- Generally safe, but can cause brief table locks on busy sites.
Analyze & Repair Tables
- Runs `CHECK TABLE` on all tables to find errors/corruption.
- Runs `REPAIR TABLE` automatically on tables reporting errors.
- Can fix common table issues.
- May take time on large databases.
Optimize Autoloaded Options
- Identifies potentially large autoloaded options based on size thresholds (e.g., > 10KB site size factor, > 100KB absolute, or significant percentage of total autoload size) and changes their `autoload` flag from `yes` to `no`.
- Excludes essential WordPress core and common plugin options to prevent breakage.
- Aims to reduce memory usage and improve load times by preventing large, non-essential data from loading on every page.
Database Structure Analysis
Clicking “Analyze Database Structure” provides an overview of your database tables.
- Categorizes tables into “WordPress Core Tables” and “Plugin & Theme Tables”.
- Shows: Table name, description (core tables only), row count, total size, overhead, engine, collation, and last update time for each table.
- Displays a summary including total tables, core vs. plugin count, total size, and total rows.
- Helps identify potentially orphaned tables from uninstalled plugins or large tables consuming space.
7. Automatic Backup and Cleanup
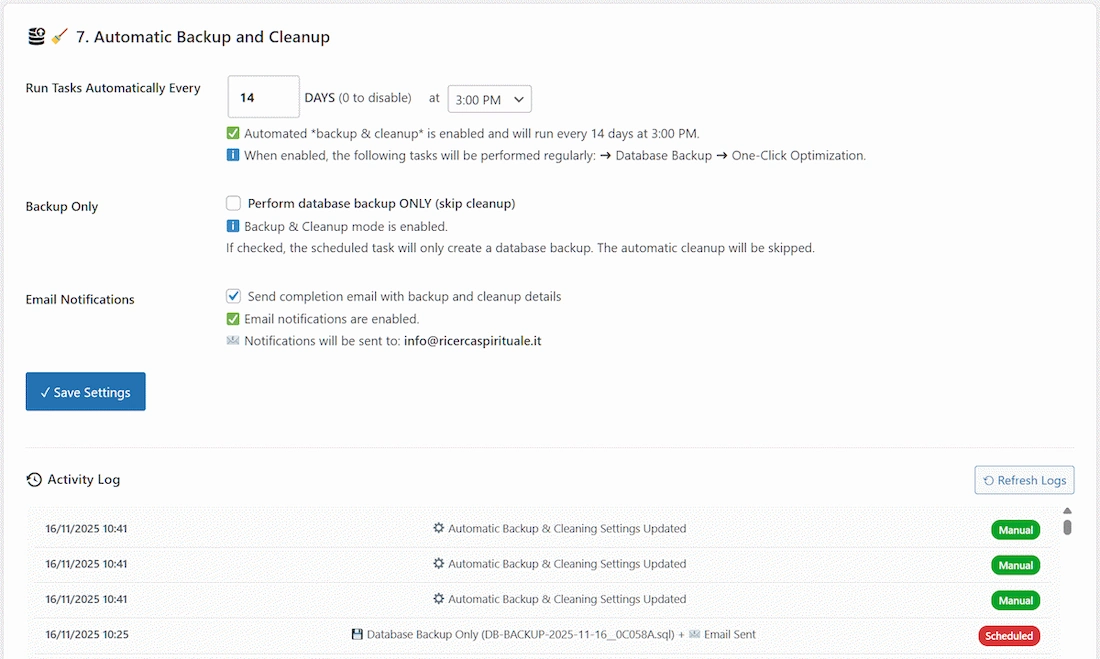
Set-it-and-forget-it optimization ⚙️
Allows configuring automated, recurring maintenance tasks.
Settings:
- Run Tasks Automatically Every: Set the frequency in days (0 to disable, 1-365).
- Time: Select the hour (on the hour, local WordPress time) for the task to run.
- Backup Only: If checked, the scheduled task will only create a database backup. The automatic cleanup will be skipped.
- Email Notifications: Checkbox to enable/disable email reports upon completion (sent to the site admin email).
- Save Settings Button: Applies the changes and schedules/unschedules the WP Cron job.
How It Works:
- When enabled, a WP Cron job (`optistate_scheduled_cleanup`) is scheduled.
- At the scheduled time, the plugin:
- Creates a new database backup (respecting the max backups limit).
- Performs the “One-Click Optimization” routine (all safe cleanups + table optimization).
- Logs the operation (visible in the Optimization Log).
- Sends an email notification if enabled and successful (or if failed).
- Reschedules the next run based on the interval.
Status Indicators:
- ✅/🔴 Green/Red text indicates if automated optimization and email notifications are currently enabled or disabled based on saved settings.
8. Performance Features Manager
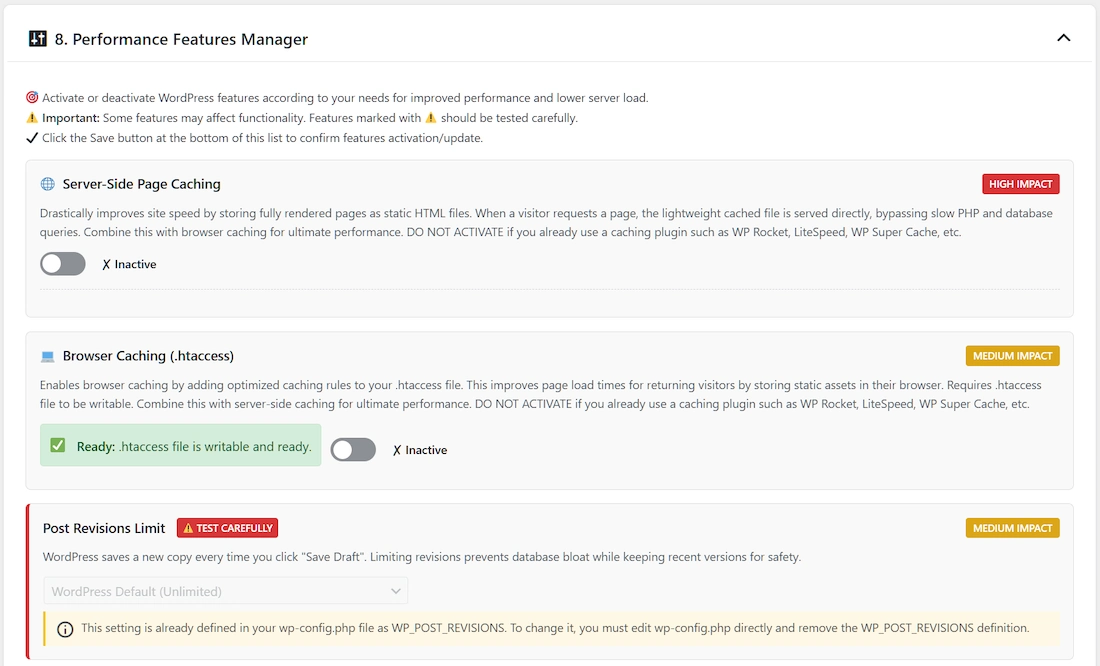
Purpose: Enhance site speed and reduce server load by disabling or modifying non-essential WordPress core features.
This section provides toggles and dropdowns to control functionalities like the Heartbeat API, post revisions, emoji scripts, XML-RPC, and various meta tags added to the site’s header.
Disabling unused features can lead to faster page loads and improved security.
Features marked with ⚠️ (like XML-RPC or disabling revisions) should be tested carefully as they can affect specific functionalities or integrations (e.g., Jetpack, remote publishing apps).
Interface: This section is collapsible. Click the header to expand or collapse the list of features.
Use the toggles or dropdowns to configure each feature and click “Save Performance Settings” at the bottom to apply changes.
🌐 Server-Side Page Caching
What It Is: Drastically improves site speed by storing fully rendered pages as static HTML files in the wp-content/uploads/optistate/page-cache/ directory.
When a visitor requests a page, the lightweight cached file is served directly, bypassing slow PHP and database queries.
Why Control It: This is one of the most effective ways to reduce Time To First Byte (TTFB) and server load.
The panel allows you to set cache lifetime, manage query strings, exclude URLs, and purge the cache.
Impact: High
Safety Level: ✅ Safe
Running two page caching systems will cause conflicts.
Browser Caching (.htaccess)
What It Is: Adds Expires Headers to your server configuration file, enabling robust browser caching for static assets (images, CSS, JS).
This is one of the most effective ways to reduce server load and improve repeat visitor load times.
Why Control It: Dramatically speeds up page loading after the first visit.
Impact: Medium
Safety Level: ✅ Safe (Basic caching system designed for maximum compatibility)
Recommendation: Confirm that content updates display properly.
⚠️ WARNING: If your server is running Nginx, this feature will not work automatically (you need to configure it manually).
These are the caching and security rules that are automatically added to the .htaccess file when this feature is activated:
👉 CLICK TO EXPAND
# BEGIN WP Optimal State Caching
# ============================================================
<IfModule mod_expires.c>
ExpiresActive On
# Default: 30 days
ExpiresDefault “access plus 30 days”
# Static Assets: 1 year
ExpiresByType image/jpg “access plus 1 year”
ExpiresByType image/jpeg “access plus 1 year”
ExpiresByType image/png “access plus 1 year”
ExpiresByType image/gif “access plus 1 year”
ExpiresByType image/webp “access plus 1 year”
ExpiresByType image/svg+xml “access plus 1 year”
ExpiresByType image/x-icon “access plus 1 year”
ExpiresByType font/woff “access plus 1 year”
ExpiresByType font/woff2 “access plus 1 year”
ExpiresByType application/font-woff “access plus 1 year”
# CSS &
JavaScript: 1 month
ExpiresByType text/css “access plus 1 month”
ExpiresByType application/javascript “access plus 1 month”
ExpiresByType application/x-javascript “access plus 1 month”
# HTML: Respect server-side caching headers
ExpiresByType text/html “access plus 24 hours”
</IfModule>
<IfModule mod_headers.c>
# Security Headers
Header always set X-Content-Type-Options “nosniff”
Header always set X-Frame-Options “SAMEORIGIN”
Header always set Referrer-Policy “strict-origin-when-cross-origin”
Header always set X-XSS-Protection “1; mode=block”
# Long cache for static assets
<FilesMatch “\.(css|js|ico|pdf|jpg|jpeg|png|gif|webp|svg|woff|woff2|eot|ttf|mp4|webm|mp3|ogg|wav|aac|m4a|flac)$”>
Header set Cache-Control “max-age=31536000, public, immutable”
</FilesMatch>
# Dynamic content
<FilesMatch “\.(php|html|htm)$”>
Header set Cache-Control “public, max-age=86400” env=!PHP_CACHE_HEADERS
</FilesMatch>
# Protect sensitive WP files
<FilesMatch “(wp-config\.php|readme\.html|license\.txt|wp-login\.php|wp-admin/|xmlrpc\.php)”>
Header set Cache-Control “no-cache, no-store, must-revalidate”
Header set Pragma “no-cache”
Header set Expires “0”
</FilesMatch>
# Ensure proper encoding handling
<FilesMatch “\.(js|css|html|htm|xml|json)$”>
Header append Vary Accept-Encoding
</FilesMatch>
# Remove ETag
Header unset ETag
FileETag None
</IfModule>
# Brotli Compression
<IfModule mod_brotli.c>
AddOutputFilterByType BROTLI_COMPRESS text/html text/plain text/css application/javascript application/json image/svg+xml application/xml
</IfModule>
# GZIP Compression
<IfModule mod_deflate.c>
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE text/plain
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE text/html
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE text/css
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE text/javascript
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE application/javascript
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE application/x-javascript
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE application/xml
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE application/xhtml+xml
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE application/rss+xml
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE application/json
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE font/woff
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE font/woff2
AddOutputFilterByType DEFLATE image/svg+xml
# Skip already compressed files
SetEnvIfNoCase Request_URI \.(?:gz|zip|bz2|rar|7z|mp4|webm|avi)$ no-gzip dont-vary
# Browser workarounds
BrowserMatch ^Mozilla/4 gzip-only-text/html
BrowserMatch ^Mozilla/4\.0[678] no-gzip
BrowserMatch \bMSIE !no-gzip !gzip-only-text/html
</IfModule>
# Disable directory listing
Options -Indexes
# Leverage Keep-Alive connections
<IfModule mod_headers.c>
Header set Connection keep-alive
</IfModule>
# END WP Optimal State Caching
# ============================================================
.htaccess file.The plugin takes every precaution for safe writing and removal.
If you already use another caching solution (e.g., LiteSpeed, Varnish, Cloudflare, or another plugin’s .htaccess rules) you should not activate this feature.
Database Query Caching
What It Is: Stores the results of frequent database queries in memory for faster retrieval.
Why Control It: Can significantly reduce database load and improve page load speed, but requires proper server support (e.g., Redis, Memcached).
Impact: High
Safety Level: ✅ Safe
Recommendation: Enable with a persistent object cache (e.g., Redis) for best performance.
Lazy Load Images & Iframes
What It Is: Delays loading off-screen images and iframes until the user scrolls near them.
Why Control It: Reduces initial page load time, saves bandwidth, and improves Core Web Vitals (LCP).
Impact: Medium
Safety Level: ✅ Safe
Recommendation: Enable for better performance.
Test for compatibility with sliders or specific gallery plugins.
🤖 Bad Bot Blocker
What It Is: Blocks resource-intensive SEO crawlers (e.g., AhrefsBot, SemrushBot, MJ12bot) that provide competitive intelligence to other businesses.
Why Control It: These bots consume significant server resources (CPU/RAM) without bringing real traffic or value. Blocking them frees up resources for legitimate visitors.
Impact: High
Safety Level: ✅ Safe
Recommendation: Enable to reduce server load. Legitimate search engines like Google, Bing, and regional engines are not blocked.
Includes a customizable list of User Agents you can edit.
Post Revisions Limit ⚠️
What It Is: WordPress saves copies of posts during editing.
Why Control It: Unlimited revisions bloat the database.
Impact: Medium
Safety Level: ⚠️ CAUTION – Affects ability to restore older versions.
Options: Default (Unlimited), Limit to 3/5/10, Disable (not recommended).
Automatic Trash Emptying ⚠️
What It Is: Recycle bin collecting removed posts and pages.
Why Control It: Hundreds of trashed items bloat the database.
Impact: Medium
Safety Level: ⚠️ CAUTION – Items cannot be restored after emptying.
Options: Default (30 days), Empty every 7/14/30/60/90 days, Disable.
Disable XML-RPC ⚠️
What It Is: API for remote connections (older apps, Jetpack).
Why Disable It: Security risk (brute-force attacks) and often unused.
Impact: Medium
Safety Level: ⚠️ CAUTION – Breaks tools relying on it (e.g., Jetpack, older mobile apps).
Recommendation: Disable unless needed for specific integrations.
Heartbeat API Control
What It Is: An API for frequent browser-server communication (AJAX) used for auto-saving, post locking, etc.
Why Control It: Can cause high CPU usage on some hosts.
Impact: High
Safety Level: ✅ Safe (Slowing down is safe; disabling can affect editor features)
Options: Default, Slow Down (2 mins), Disable in Admin, Disable Frontend, Disable Everywhere.
Disable Emoji Scripts
What It Is: JavaScript for emoji support in older browsers.
Why Disable It: Redundant in modern browsers, adds an unnecessary request.
Impact: Low
Safety Level: ✅ Safe
Recommendation: Safe to disable.
Disable Self Pingbacks
What It Is: Notifications when linking to your own site’s posts.
Why Disable It: Creates unnecessary database/comment clutter.
Impact: Low
Safety Level: ✅ Safe
Recommendation: Safe to disable.
Remove Other Header Links
What They Are: WordPress adds several informational links to the <head> section of your site’s HTML, which are often unnecessary.
Why Disable Them: Removing them cleans up your site’s code and removes a small amount of page weight.
Impact: Low
Safety Level: ✅ Safe
Available Toggles:
- REST API Link: Removes the discovery link for the REST API.
The API itself will still work. - Shortlink Tag: Removes the link to the short version of the URL (e.g., `/?p=123`).
- RSD (Really Simple Discovery) Link: Used by external blog clients.
Safe to remove unless you use desktop blogging software. - Windows Live Writer Manifest: For a discontinued blogging application.
Safe to remove. - WordPress Version Meta Tag: Removes the tag that displays your current WordPress version.
This is a good security practice to hide your version from potential attackers.
9. Settings Export & Import

Expandable Section
This utility allows you to save all your plugin configurations (from Section 1, 7, 8) to a single .json file. You can use this to create a backup of your settings or to quickly migrate your exact setup to another website.
This feature only exports the plugin’s settings, such as your configurations for scheduled tasks and performance features. It does NOT export your database backups, cached pages, or activity logs. Always download your .sql.gz backups separately from Section 1.
How to Export Settings:
- Click the “Export Settings” button.
- Your browser will download a file named
optistate-settings-YYYY-MM-DD-His.json. - Keep this file in a safe place.
How to Import Settings:
- Click the “Choose JSON File” button and select the
.jsonfile you previously exported. - The plugin validates the file. It must be a valid
.jsonfile, under 1MB, and contain the “WP Optimal State” signature. - Once validated, click the “Import Settings” button.
- A confirmation pop-up will appear warning you that your current settings will be overwritten. Click “OK” to proceed.
- After a successful import, you will be prompted to reload the page to see the new settings take effect.
ℹ️ Please Note: This will completely overwrite all your current plugin settings. This is useful for restoring your configuration after an update or for setting up a new site.
Features & Functions
One-Click Optimization
Purpose: Perform all safe database maintenance in one action
What It Does:
- Removes all post revisions
- Deletes auto-draft posts
- Cleans trashed posts
- Cleans spam comments
- Removes trashed comments
- Deletes orphaned post metadata
- Removes orphaned comment metadata
- Cleans orphaned term relationships
- Deletes expired transients
- Removes duplicate post metadata
- Removes duplicate comment metadata
- Removes orphaned user metadata
- Deletes pingbacks and trackbacks
- Optimizes all database tables (`OPTIMIZE TABLE`)
Process: Click “Optimize Now”, wait, review results. Statistics refresh automatically.
Safety Level: ✅ Safe – Primarily affects unneeded or deleted data.
Recommended Frequency: Weekly or bi-weekly.
Individual Cleanup Operations
Post Revisions
What It Is: WordPress automatically saves versions of your posts and pages every time you edit them
Why Clean: Each revision is stored as a separate post in the database, potentially creating hundreds or thousands of entries
Safety Level: ✅ Safe – Deleting revisions removes historical versions but doesn’t affect the current published post. Consider limiting revisions instead if you need history.
When to Clean:
- Before major database operations
- When revision count is very high
- If you don’t use the revision feature
Impact: Can significantly reduce database size on content-heavy sites.
Auto Drafts
What It Is: WordPress automatically saves draft posts as you type
Why Clean: Abandoned posts remain as auto-drafts indefinitely
Safety Level: ✅ Safe – Only removes abandoned drafts not manually saved.
When to Clean: Monthly or when count exceeds 50
Impact: Minimal database size reduction but improves post list clarity.
Trashed Posts
What It Is: Posts moved to trash but not permanently deleted
Why Clean: Trash doesn’t empty automatically by default in WordPress.
Safety Level: ⚠️ CAUTION – Permanently deletes posts from the trash.
When to Clean:
- After reviewing trash contents
- When certain items should be permanently removed
- During major site cleanup
Impact: Varies based on trash contents.
⚠️ Warning: This action cannot be undone. Review trash contents first via Posts → All Posts → Trash.
Spam Comments
What It Is: Comments marked as spam by Akismet or manual moderation
Why Clean: Spam accumulates quickly on popular sites
Safety Level: ✅ Safe – Legitimate comments not affected.
When to Clean: Weekly or when spam count exceeds 100
Impact: Can significantly reduce comment table size on spam-heavy sites.
Trashed Comments
What It Is: Comments moved to trash but not permanently deleted
Why Clean: Trash doesn’t empty automatically.
Safety Level: ✅ Safe – Only deletes comments already in the trash.
When to Clean: Monthly or when count is high
Impact: Moderate database size reduction.
Orphaned Post Meta
What It Is: Custom fields and metadata entries (`wp_postmeta`) whose associated post (`wp_posts`) no longer exists.
Why Clean: When posts are deleted, their metadata sometimes remains, causing bloat.
Safety Level: ✅ Safe – Only affects metadata for non-existent posts.
When to Clean: After bulk post deletions or monthly maintenance
Impact: Can reduce `wp_postmeta` table size.
Orphaned Comment Meta
What It Is: Metadata entries (`wp_commentmeta`) whose associated comment (`wp_comments`) no longer exists.
Why Clean: Reduces `wp_commentmeta` table bloat.
Safety Level: ✅ Safe – Only affects metadata for non-existent comments.
When to Clean: After comment cleanup or monthly
Impact: Minor database size reduction.
Orphaned Relationships
What It Is: Entries in `wp_term_relationships` linking terms (tags, categories) to objects (like posts) that no longer exist in `wp_posts`.
Why Clean: Keeps taxonomy relationship tables clean and accurate.
Safety Level: ✅ Safe – Only removes relationships for deleted posts/objects.
When to Clean: After bulk deletions or quarterly
Impact: Minor database size reduction.
Expired Transients
What It Is: Temporary cached data stored in `wp_options` whose expiration time has passed.
Why Clean: WordPress has a built-in cleanup, but it doesn’t always run reliably, leaving expired data behind.
Safety Level: ✅ Safe – Only removes data explicitly marked as expired.
When to Clean:
- Weekly as preventive maintenance
- When `wp_options` table is large
- After deactivating plugins that use transients
Impact: Can significantly reduce `wp_options` table size.
All Transients
What It Is: All temporary cached data stored in `wp_options` (entries starting with `_transient_` or `_site_transient_`), including both expired and active transients.
Why Clean: Forces WordPress and plugins to regenerate fresh cached data. Useful for troubleshooting caching issues.
Safety Level: ⚠️ CAUTION – May temporarily slow down your site significantly while caches are rebuilt.
When to Clean:
- When troubleshooting caching-related problems
- After major plugin updates if issues occur
- If site displays stale or incorrect data suspected to be from transients
Impact: Temporarily increases page generation time and server load.
⚠️ Warning: Site may be slower for a period (minutes to hours depending on traffic and complexity) while cache rebuilds.
Duplicate Post Meta
What It Is: Identical entries (same `post_id`, `meta_key`, and `meta_value`) in the `wp_postmeta` table. Only the oldest entry (lowest `meta_id`) is kept.
Why Clean: Database errors or plugin bugs can sometimes create duplicate metadata, wasting space and potentially causing minor inconsistencies.
Safety Level: ✅ Safe – Removes redundant exact duplicates, keeping one original copy.
When to Clean:
- During annual deep cleanup
- If `wp_postmeta` table is unusually large and duplicates are suspected
Impact: Varies depending on duplicate count, usually minor.
Duplicate Comment Meta
What It Is: Identical entries (same `comment_id`, `meta_key`, `meta_value`) in the `wp_commentmeta` table. Only the oldest entry is kept.
Why Clean: Similar to duplicate post meta, cleans up redundancy.
Safety Level: ✅ Safe – Removes redundant exact duplicates.
When to Clean: During thorough database maintenance.
Impact: Usually minor database size reduction.
Orphaned User Meta
What It Is: Metadata entries (`wp_usermeta`) whose associated user (`wp_users`) no longer exists.
Why Clean: Keeps `wp_usermeta` table clean after users are deleted.
Safety Level: ✅ Safe – Only affects metadata for non-existent users.
When to Clean:
- After removing spam users
- After bulk user deletions
- Quarterly maintenance
Impact: Depends on user deletion history.
Unapproved Comments
What It Is: Comments submitted but awaiting moderation approval (`comment_approved = 0`).
Why Clean: Useful for quickly removing a large backlog of pending comments, often spam that wasn’t caught.
Safety Level: ⚠️ CAUTION – Permanently deletes comments that might be legitimate but haven’t been approved yet.
When to Clean:
- When moderation queue is overwhelmingly large with spam
- After manually reviewing pending comments and deciding to bulk delete
Impact: Varies based on comment volume.
⚠️ Warning: Review pending comments first via Comments → Pending if you suspect legitimate comments might be present.
Pingbacks
What It Is: Notifications created when another WordPress site links to your content (`comment_type = ‘pingback’`).
Why Clean: Many pingbacks are spam or noise; often disabled on modern sites.
Safety Level: ✅ Safe – Won’t affect regular user comments.
When to Clean:
- If you don’t use or want pingbacks
- When pingback spam is high
- During comment cleanup
Impact: Reduces `wp_comments` table size.
Trackbacks
What It Is: Similar to pingbacks but using an older notification protocol (`comment_type = ‘trackback’`).
Why Clean: Rarely used now; mostly spam.
Safety Level: ✅ Safe – Won’t affect regular user comments.
When to Clean: Anytime, especially if not using trackbacks.
Impact: Minor database size reduction.
Database Table Optimization
Optimize All Tables
What It Does:
- Runs MySQL `OPTIMIZE TABLE` command on all database tables.
- Reclaims unused space (overhead) resulting from deleted or updated rows.
- Defragments table data and indexes for potentially better performance.
- Updates index statistics for the query optimizer.
- May perform implicit repair actions on some table types (like MyISAM).
Technical Process: Executes `OPTIMIZE TABLE table_name;` for each table in the database.
The exact behavior depends on the storage engine (e.g., InnoDB, MyISAM).
When to Use:
- After cleaning large amounts of data (e.g., deleting many posts or comments).
- As part of regular monthly maintenance.
- If database statistics show significant table overhead (`data_free`).
Duration: Can range from seconds to many minutes depending on the size and number of tables.
Large tables will take longer.
Safety Level: ✅ Safe – Non-destructive operation.
However, tables are typically locked during optimization, which can cause temporary unresponsiveness on very busy sites. Run during low-traffic periods.
Expected Results:
- Reduction in reported database overhead.
- Potentially improved query performance, especially on fragmented tables.
- Database file size may or may not decrease immediately (especially with InnoDB).
Analyze & Repair Tables
What It Does:
- Runs MySQL `CHECK TABLE` command on all tables to diagnose errors, corruption, or inconsistencies.
- If `CHECK TABLE` reports errors for a table, it automatically runs `REPAIR TABLE` on that specific table.
- Aims to fix structural problems within tables.
Technical Process: Executes `CHECK TABLE table_name;` for all tables.
If errors are found, executes `REPAIR TABLE table_name;`.
When to Use:
- If you encounter “database error” messages on your site.
- After unexpected server shutdowns, crashes, or power outages.
- As part of quarterly or annual preventive maintenance.
- If specific tables are suspected of being corrupted.
Duration: Can range from seconds to many minutes, especially if repairs are needed on large tables.
Safety Level: ✅ Safe – `CHECK TABLE` is read-only.
`REPAIR TABLE` attempts to fix issues but should always be preceded by a backup, as complex corruption might not be fully repairable.
Expected Results:
- Identification and correction of table corruption issues.
- Prevention of potential data loss due to table damage.
- Improved database stability.
Note: `REPAIR TABLE` is most effective on MyISAM tables.
For InnoDB, it mainly checks for corruption; more severe InnoDB issues might require different recovery methods (like restoring from backup).
Optimize Autoloaded Options
What It Does:
- Queries the `wp_options` table for rows where `autoload = ‘yes’`.
- Identifies options exceeding specific size thresholds (considering absolute size and relative size compared to total autoload data).
- Updates the `autoload` flag for these large options from `yes` to `no`.
- Excludes a predefined list of essential WordPress core and common plugin options (e.g., `active_plugins`, `siteurl`, `theme_mods_*`, `widget_*`, `woocommerce_*`, `elementor_*`, `wpseo*`) to prevent breaking critical site functionality.
Why It Matters: Options marked `autoload = ‘yes’` are loaded by WordPress on every single page load, whether they are needed on that specific page
or not. Loading numerous or very large options into memory unnecessarily can significantly slow down page generation and increase server resource consumption.
Converting large, non-essential options to `autoload = ‘no’` means they will only be loaded by WordPress when explicitly requested by a plugin or theme using `get_option()`.
What’s Considered Large: The plugin uses dynamic thresholds, but generally targets options larger than ~10KB-100KB, especially those making up a significant portion of the total autoload size.
When to Use:
- If the “Autoloaded Options Size” statistic is high (e.g., over 800KB – 1MB).
- As part of regular monthly or quarterly performance tuning.
- After installing/uninstalling plugins that might store large amounts of data in options.
- If experiencing high memory usage or slow backend performance.
Safety Level: ✅ Safe – The exclusion list protects most critical options.
Poorly coded themes/plugins might theoretically break if they expect a large option they store to always be autoloaded, but this is rare.
Expected Results:
- Reduced memory usage per page load.
- Potentially faster page generation times (especially TTFB – Time To First Byte).
- More responsive WordPress admin area.
Database Structure Analysis
What It Does:
- Analyzes the database architecture to categorize tables into “WordPress Core” and “Plugin/Theme”.
- Calculates total table count, size, and row counts for each category.
- Provides detailed insights for every table, including engine type, collation, and size breakdown (data vs. index).
- Identifies potentially “abandoned” tables that haven’t been updated in over 30 days.
Why It Matters: Helps you understand what is consuming your database space and identify leftover tables from uninstalled plugins.
Technical Process: Queries `information_schema.TABLES` to retrieve metadata. Compares table names against a known list of WordPress core tables (e.g., `wp_posts`, `wp_options`, `wp_users`) to separate core data from third-party data.
Safety Level: ✅ Safe – This is a read-only analysis operation.
Note: Deleting tables via this tool (if available) is a destructive action and should only be done after verifying the table is truly unused and backing up the database.
MySQL Index Manager
What It Does:
- Scans your database for missing high-impact indexes that can drastically improve query performance.
- Checks critical tables like `wp_options`, `wp_postmeta`, `wp_posts`, and `wp_usermeta`.
- Allows you to add recommended indexes with a single click.
Why It Matters: Missing indexes force MySQL to scan full tables instead of jumping directly to the data, which causes slow queries and high server load. Adding indexes like `autoload` on `wp_options` can reduce query time by up to 90%.
Technical Process:
- Checks `wp_options` for an index on `autoload` and a composite index on `autoload, option_name`.
- Checks `wp_postmeta` for indexes on `meta_key` and composite `post_id, meta_key`.
- Checks `wp_posts` for composite indexes on `post_type, post_status, post_date` and `post_type, ID`.
- Checks `wp_usermeta` for a composite index on `user_id, meta_key`.
Safety Level: ✅ Safe – Adding indexes optimizes the database structure without altering or deleting any data.
Database Search & Replace
What It Does:
- Searches the entire database (or selected tables) for a specific text string and replaces it with another.
- Safely handles WordPress serialized data (arrays and objects stored as text), ensuring they are unserialized, modified, and re-serialized correctly to prevent breaking widgets or theme settings.
- Offers a “Dry Run” mode to preview matches and potential changes before executing.
When to Use:
- Migrating a site to a new domain (replacing `old-domain.com` with `new-domain.com`).
- Switching from HTTP to HTTPS (replacing `http://` with `https://`).
- Updating paths or specific content strings across all posts and settings.
Features:
- Case Sensitivity: Option to perform case-sensitive searches (e.g., “Apple” vs “apple”).
- Partial Match: Option to search for partial text segments or require exact word boundaries.
- Table Selection: Ability to target specific tables or run on the entire database.
Safety Level: ⚠️ Advanced Feature – Use with Caution.
This operation modifies data irreversibly.
Recommendation: Always perform a “Dry Run” first to verify matches, and create a fresh database backup immediately before clicking “Execute Replacement”.
Automated Cleaning Scheduler
Purpose: Set up fully automated database maintenance that runs on your preferred schedule.
Configuration Options:
- Field: Number input for frequency (0-365 days).
- Time Selector: Dropdown to select the hour (local WordPress time) for execution.
- Email Notification Checkbox: Enable/disable completion/failure reports.
- Default: 0 days (disabled).
How Automated Cleaning Works:
- Scheduling: Uses WordPress Cron (`wp_schedule_single_event`) to schedule the `optistate_scheduled_cleanup` hook.
- Execution: When the cron job triggers, it:
- Creates a database backup (`create_backup_silent`).
- Performs the “One-Click Optimization” routine (`perform_optimizations`).
- Logs the event.
- Sends email notification if enabled (`send_scheduled_cleanup_notification` or `send_scheduled_failure_notification`).
- Reschedules the next event based on the configured interval.
- Safety: Backup is always created before cleanup attempts. Failed backups prevent cleanup. Failed cleanups trigger failure notifications.
Recommended Settings by Site Type:
| Site Type | Recommended Interval | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| High-traffic Blog | 7 days | Frequent content updates and comments generate revisions, transients, etc. |
| E-commerce | 7-14 days | Order data, customer sessions, transients accumulate. |
| Business Website | 14-30 days | Moderate content changes, form entries, transients. |
| Portfolio/Brochure | 30-90 days | Infrequent updates, less data accumulation. |
Setup Instructions:
- Navigate to Section 7: Automatic Backup and Cleanup.
- Enter desired interval in days (e.g., 7).
- Select preferred time from dropdown.
- Check “Email Notifications” box if desired.
- Click “Save Settings”.
- Verify status indicator updates correctly.
Status Monitoring: Check the status indicators below the settings. The plugin log (accessible via AJAX, not directly displayed in UI by default) records automated runs. Automated backups appear in the backup list (Section 1.1).
Safety Guidelines
Before You Start
Essential Pre-Cleanup Steps
- Create Full Database Backup
- Use the integrated backup feature (Section 1).
- Strongly Recommended: Download the backup to your local computer.
- Consider using an additional backup method (hosting backup, dedicated plugin) for redundancy.
- Test on Staging Site First (Highly Recommended for Major Cleanups)
- If available, clone your site to a staging environment.
- Run the intended cleanup/optimization operations there.
- Thoroughly test site functionality on staging after cleanup.
- Apply to the live site only after successful staging tests.
- Review Current Statistics & Health Score
- Understand the current state of your database (Section 4).
- Check the Health Score and recommendations (Section 3).
- Note the counts for items you plan to clean.
- Schedule Maintenance Window (For Manual Operations)
- Choose a time with minimal website traffic.
- Inform relevant team members or stakeholders.
- Allocate sufficient time (allow extra for backups/unexpected issues).
- Understand the Operation
- Read the description for each cleanup item you intend to run (Section 5).
- Pay close attention to items marked with ⚠️ (Caution Required).
Understanding Risk Levels
✅ Safe Operations (Generally Low Risk)
These operations primarily target data that is typically redundant, temporary, already deleted, or not directly visible on the live site. While backups are always recommended, these are unlikely to break site functionality.
- Post revisions
- Auto drafts
- Spam comments
- Trashed comments
- Orphaned metadata (all types)
- Expired transients
- Pingbacks
- Trackbacks
- Duplicate metadata
- Database table optimization (`OPTIMIZE TABLE`)
- Analyze & Repair Tables (`CHECK TABLE`, `REPAIR TABLE`) – Repair carries minimal risk but fixes existing issues.
- Optimize Autoloaded Options (due to exclusion list)
- Performance Feature: Server-Side Page Caching (if no other cache plugin is active)
- Performance Feature: Browser Caching (.htaccess) (if no other cache plugin is active)
- Performance Feature: Disable Emoji Scripts
- Performance Feature: Disable Self Pingbacks
- Performance Feature: Remove Header Links
(REST API, Shortlink, RSD, WLW Manifest, WP Version)
Recommendation: Run regularly, always preceded by a backup for best practice.
⚠️ Caution Required (Moderate Risk)
These operations permanently delete data that could potentially be needed later, or might temporarily affect site performance. Review carefully before proceeding.
- Trashed Posts: Permanently deletes posts/pages from the trash. Ensure nothing important is in the trash first.
- All Transients: Clears active cache data. Can cause temporary site slowdown while caches rebuild. Usually safe, but can affect performance temporarily.
- Unapproved Comments: Permanently deletes comments awaiting moderation. Ensure no legitimate comments are pending approval.
- Performance Feature: Heartbeat API Control (Disabling can affect editor features like locking/autosave).
- Performance Feature: Post Revisions Limit (Disabling removes history).
- Performance Feature: Disable XML-RPC (Breaks integrations relying on it, e.g., Jetpack, older apps).
Recommendation: Understand the implications. Backup is essential. Review relevant sections (Trash, Pending Comments) before running. Test performance feature changes.
🛑 High Risk Operations (Not Performed by This Plugin)
WP Optimal State deliberately avoids actions that directly modify core published content or critical site structure without explicit user action elsewhere in WordPress:
- Deleting published posts/pages (use WordPress Trash).
- Removing approved, non-spam comments (use WordPress moderation).
- Modifying user accounts or roles (use WordPress Users section).
- Changing core WordPress settings (use WordPress Settings section).
- Deleting or modifying media files (use Media Library).
- Dropping unknown database tables (requires manual action via tools like phpMyAdmin).
Recommendation: Perform these actions through standard WordPress interfaces or dedicated tools, always with caution and backups.
Recovery Procedures
If Something Goes Wrong After Cleanup/Optimization
1. Stay Calm & Assess
- What operation did you just perform?
- What specific issue are you seeing (e.g., white screen, error message, missing content)?
- Is the issue site-wide or specific to certain pages/functions?
- Note any error messages precisely.
2. Restore Your Most Recent Backup
This is the quickest and most reliable way to revert changes.
- Method 1: Using WP Optimal State Restore (Recommended if backup was made with the plugin)
- Navigate to Section 1.1: Manage Existing Backups.
- Identify the backup made before the problematic operation.
- Click the “Restore” button next to it.
- Confirm the action in the modal window.
- The plugin will handle the safe restore process (including safety backup and atomic swap).
- Method 2: Using Hosting Provider Backup/Restore
- Access your hosting control panel (cPanel, Plesk, custom dashboard).
- Find the backup management section.
- Select the database backup created before the operation.
- Follow your host’s instructions to restore the database.
- Method 3: Using a Backup Plugin (e.g., UpdraftPlus)
- Go to your backup plugin’s settings page.
- Find the backup created before the operation.
- Initiate the restore process (usually involves selecting the database component).
- Method 4: Manual Restore via phpMyAdmin (Advanced)
- Access phpMyAdmin through your hosting panel.
- Select your WordPress database.
- Select all tables and choose “Drop” to empty the database (DANGEROUS! Ensure you have the correct backup file!).
- Click the “Import” tab.
- Upload the `.sql.gz` backup file created before the operation.
- Execute the import.
3. Verify Site Functionality After Restore
- Clear your browser cache and any server-side caches (WP Rocket, host cache, etc.).
- Check if the homepage and key pages load correctly.
- Test logging into the WordPress admin area.
- Verify that posts, pages, and comments appear as expected.
- Test critical functionality (e.g., contact forms, e-commerce checkout).
4. Investigate the Cause (Optional, After Recovery)
- Review which specific operation caused the issue.
- Check WordPress debug logs (`wp-content/debug.log`) if debug mode was enabled.
- Check server error logs (PHP error log, MySQL error log).
- Consider plugin or theme conflicts.
5. Contact Support if Needed
- If restoration fails or you need help identifying the cause, contact plugin support, your hosting provider, or a WordPress developer. Provide details about the operation performed, the issue encountered, and steps taken.
Best Practices for Safe Operation
Follow a routine to minimize risks and maximize benefits.
Routine Checks (Daily/Weekly)
- Monitor Database Health Score and Statistics for sudden changes.
- Ensure automated backups (plugin, host, or other) are running successfully.
Regular Maintenance (Weekly/Bi-Weekly)
- Create a fresh backup.
- Run One-Click Optimization (or use the Automated Scheduler).
- Quickly review site functionality post-cleanup.
Thorough Maintenance (Monthly/Quarterly)
- Create and download a backup.
- Consider testing on staging first.
- Run individual safe cleanup operations (Section 5).
- Run “Optimize Autoloaded Options” (Section 6).
- Run “Optimize All Tables” (Section 6).
- Run “Analyze & Repair Tables” (Section 6).
- Review operations marked with ⚠️ (Trashed Posts, All Transients, Unapproved Comments) and run only if necessary after manual review.
- Review Performance Features Manager settings (Section 8).
- Thoroughly check site functionality post-cleanup.
General Principles
- Backup Redundancy: Don’t rely solely on one backup method.
- Test Backups: Periodically test restoring a backup to ensure they are valid.
- Low Traffic Periods: Perform manual cleanups and restores during off-peak hours.
- Document Changes: Keep a log of major cleanup operations performed.
- Stay Updated: Keep WordPress core, themes, and plugins (including WP Optimal State) updated.
Troubleshooting
Common Issues and Solutions
Issue: “Unauthorized” or “Nonce verification failed” Error
Symptoms: Error message when clicking buttons, operations fail, stats don’t load.
Causes: User lacks administrator permissions, WordPress login session expired, security token (nonce) mismatch, caching issues, security plugin interference.
Solutions:
- Log out of WordPress and log back in.
- Hard refresh the WP Optimal State page in your browser (Ctrl+F5 or Cmd+Shift+R).
- Clear your browser’s cache and cookies.
- Ensure your user account has the ‘Administrator’ role.
- Temporarily disable any security or caching plugins to check for conflicts.
- Try accessing the page in a different web browser or incognito/private window.
Issue: Statistics Not Loading or Stuck Loading
Symptoms: “Loading…” message persists, empty stats panel, spinner doesn’t stop.
Causes: Large database taking time to query, JavaScript conflict with another plugin/theme, server timeout during AJAX request, database connection issue, browser issue.
Solutions:
- Wait longer (up to 1-2 minutes) if your database is very large.
- Click the “Refresh Stats” button.
- Hard refresh the page (Ctrl+F5 or Cmd+Shift+R).
- Check your browser’s developer console (F12 key) for JavaScript errors. Note any errors mentioning `admin.js` or AJAX failures.
- Temporarily switch to a default WordPress theme (like Twenty Twenty-Three) and disable other plugins (except WP Optimal State) to check for conflicts. Reactivate one by one to find the cause.
- Check your web hosting control panel for database status or errors.
- Contact hosting support to inquire about potential server-side timeouts or resource limits affecting AJAX requests.
Issue: Operation Times Out (e.g., Cleanup, Optimize, Backup, Restore)
Symptoms: Process gets stuck, white screen appears, server error message (e.g., “504 Gateway Timeout”, “Maximum execution time exceeded”).
Causes: Operation requires more processing time than allowed by PHP (`max_execution_time`) or the webserver, insufficient PHP memory (`memory_limit`), very large database tables being processed, server resource limitations (CPU, I/O).
Solutions:
- For Cleanups: Try cleaning items individually or in smaller groups instead of using One-Click Optimization.
- Increase Server Limits:
- Contact your hosting provider and ask them to increase `max_execution_time` (e.g., to 300 or 600 seconds) and `memory_limit` (e.g., to 256M or 512M) in your PHP configuration.
- Alternatively, you might be able to set these via `.htaccess`, `php.ini`, or `wp-config.php` (though hosting overrides may apply):
// In wp-config.php (try adding before /* That's all, stop editing! */) @ini_set('max_execution_time', '300'); // 300 seconds = 5 minutes @ini_set('memory_limit', '256M');
- Use WP-CLI: For very large databases, performing optimizations via WP-CLI (command line) often bypasses web server timeouts. Use commands like `wp db optimize`, `wp transient delete –expired`, etc.
- Run During Off-Peak Hours: Less server load might allow operations to complete.
- Upgrade Hosting: If resource limits are consistently hit, your hosting plan might be insufficient.
Issue: Database Size Doesn’t Decrease After Cleanup
Symptoms: Cleanup reports items deleted, but “Total Database Size” statistic remains similar.
Causes:
- Table Optimization Needed: Deleting rows marks space as reusable but doesn’t always shrink the physical file size immediately. Running “Optimize All Tables” is usually required to reclaim this space.
- Storage Engine Behavior: InnoDB (common default) manages space internally and might not shrink table files (`.ibd`) on disk even after optimization, preferring to reuse the freed space for future inserts/updates. The usable space increases, but reported file size might not drop significantly. MyISAM tables tend to shrink more readily.
- Overhead vs. Data: The cleaned items might represent only a small fraction of the total database size, which includes essential content (posts, users, settings) and plugin data.
Solutions:
- Run “Optimize All Tables”: This is the most crucial step after deleting data.
- Check Overhead Stat: Monitor the “Database Overhead” statistic. A successful optimization should reduce this value, even if total size doesn’t drop dramatically.
- Wait: Sometimes background processes or future operations allow the database engine to better utilize freed space.
- Focus on Large Data Types: If size is a major concern, focus on cleaning items that consume the most space (often revisions, spam comments, or large transients/options). Use the Database Structure Analysis tool to identify large tables.
Issue: Site Slower After Cleaning “All Transients”
Symptoms: Pages load noticeably slower immediately after running the “Clean All Transients” operation.
Causes: This operation deletes ALL transient cache data, including currently active and valid caches used by WordPress core, themes, and plugins for performance. The site slows down because this data needs to be regenerated, often requiring fresh database queries or computations.
Solutions:
- Wait: This is usually temporary. As you and visitors browse the site, caches will be rebuilt, and performance should return to normal or potentially improve (if old/stale transients were causing issues). This might take minutes to hours depending on site traffic and complexity.
- Manually Trigger Cache Rebuilding: Visit key pages of your site (homepage, popular posts, archives) to encourage faster cache regeneration.
- Clear Other Caches: Clear page caches (WP Rocket, W3TC, etc.) and object caches (Redis, Memcached) if you use them, as they might interact with transients.
- Clear Browser Cache: Ensure you’re not seeing a locally cached slower version.
Prevention: Only use “Clean All Transients” when specifically troubleshooting caching issues. For regular maintenance, use “Clean Expired Transients”.
Issue: Cannot Access Admin Area After Restore (“White Screen”, Errors)
Symptoms: After attempting a database restore, you can no longer log in or access `/wp-admin/`. You might see a blank white screen, a database connection error, or other critical PHP errors.
Causes: Restore failed partway through, restored backup was corrupted or incompatible (e.g., wrong site prefix, different WP version, missing critical tables/options), database connection details became incorrect, file permissions issue.
Solutions:
- Restore Backup (External Method): This is the most critical step. Use your hosting provider’s backup tool, another backup plugin, or manual phpMyAdmin import to restore the backup you made before attempting the WP Optimal State restore.
- Check `wp-config.php`: Ensure database connection details (DB_NAME, DB_USER, DB_PASSWORD, DB_HOST, table_prefix) are correct and match the restored database.
- Enable Debug Mode: Add the following lines to `wp-config.php` (before `/* That’s all… */`) to see specific error messages instead of a white screen:
define('WP_DEBUG', true); define('WP_DEBUG_LOG', true); // Errors logged to wp-content/debug.log define('WP_DEBUG_DISPLAY', true); // Display errors on screen (use cautiously on live sites) @ini_set('display_errors', 'On');Note the errors displayed or check `wp-content/debug.log` via FTP/File Manager. Remember to remove/disable these lines after fixing the issue.
- Repair Database: Add `define(‘WP_ALLOW_REPAIR’, true);` to `wp-config.php` and visit `yoursite.com/wp-admin/maint/repair.php`. Run the repair tool. Remove the line from `wp-config.php` afterwards.
- Check File Permissions: Ensure WordPress core files and directories have appropriate permissions (typically 755 for directories, 644 for files).
- Rename Plugins/Themes Folders: Access your site via FTP or File Manager. Rename the `wp-content/plugins` folder to something like `plugins_old`. Try accessing wp-admin. If it works, a plugin was the issue. Rename the folder back and reactivate plugins one by one. You can do the same for the active theme folder within `wp-content/themes`.
- Contact Hosting Support: They can check server logs, database integrity, and assist with restoring backups.
Issue: “Clean Now” Button Does Nothing
Symptoms: Clicking button has no visual effect, no loading indicator, no success/error message.
Causes: JavaScript error preventing the button’s action, conflict with another plugin/theme’s JavaScript, browser issue (e.g., extensions blocking scripts), necessary JS file not loaded correctly.
Solutions:
- Hard refresh the page (Ctrl+F5 or Cmd+Shift+R).
- Check the browser’s developer console (F12) for JavaScript errors immediately after clicking the button.
- Temporarily disable browser extensions (especially ad blockers or script blockers).
- Try a different web browser.
- Clear browser cache.
- Temporarily switch to a default WordPress theme and disable other plugins to check for conflicts.
Issue: Some Items Won’t Clean (Count Doesn’t Decrease or Error Occurs)
Symptoms: Clicking “Clean Now” seems to run, but the item count remains unchanged, or an error message appears.
Causes: Insufficient database user permissions (lacks DELETE privilege), database table corruption preventing deletion, foreign key constraints blocking deletion (less common in standard WP tables), specific item is protected or locked by another process, server-side error during the delete query.
Solutions:
- Check Permissions: Ensure the database user defined in `wp-config.php` has necessary privileges (SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, ALTER, etc.). Contact your host if unsure.
- Repair Database: Run the “Analyze & Repair Tables” function within WP Optimal State (Section 6), or use the WordPress database repair tool (`define(‘WP_ALLOW_REPAIR’, true);` in `wp-config.php`, then visit `yoursite.com/wp-admin/maint/repair.php`).
- Check Logs: Enable WP_DEBUG and check `debug.log`. Also check PHP and MySQL error logs on the server for more specific database errors.
- Manual Deletion (Advanced): Try deleting a single problematic item manually via phpMyAdmin to see if a more specific error occurs. Be very careful with manual SQL commands.
- Contact Hosting Support: They can investigate database-level issues or permission problems.
Error Messages Explained
| Error Message (or similar) | Common Meaning | Common Solution(s) |
|---|---|---|
| “Unauthorized” / “Insufficient permissions” | User role doesn’t have ‘manage_options’ capability. | Log in as an Administrator. |
| “Nonce verification failed” / “Security check failed” | Security token expired or invalid (prevents CSRF). | Refresh the page and try again; clear browser cache. |
| “Cleanup failed” / “Operation failed” / SQL Error message | Database query execution error (permissions, corruption, syntax). | Check permissions; run Analyze/Repair; check debug/server logs for specific SQL error. |
| “Maximum execution time exceeded” | PHP script took too long to run. | Increase `max_execution_time`; clean smaller batches; use WP-CLI. |
| “Allowed memory size exhausted” / “Out of memory” | PHP script required more memory than allocated. | Increase `memory_limit`. |
| “Error establishing database connection” | WordPress cannot connect to the MySQL server. | Check `wp-config.php` credentials; check if MySQL server is running; contact hosting. |
| “Table ‘…’ doesn’t exist” | Database corruption or incomplete restore/migration. | Run database repair; restore from a known good backup. |
| “Backup failed: Directory not writable” | The server cannot write files to the backup directory. | Check file permissions for `wp-content/uploads/optistate/db-backups/` (should be writable, e.g., 755 or 775); check disk space. |
| “Restore failed: Checksum mismatch” / “Verification failed” | The selected backup file is corrupted or has been altered. | Do not restore this file. Use a different, valid backup. Delete the corrupted one. |
| “AJAX error” / Red error box with no specific message | Generic error during background request (timeout, server error, JS conflict). | Check browser console (F12) for errors; check server logs; try conflict testing. |
Debug Mode
If you encounter persistent issues, enabling WordPress debug mode can provide more detailed error information.
How to Enable:
- Connect to your site via FTP or your hosting File Manager.
- Locate and edit the `wp-config.php` file in your WordPress root directory.
- Find the line that says:
define( 'WP_DEBUG', false ); - Change `false` to `true`.
- Add the following lines directly below it:
define( 'WP_DEBUG_LOG', true ); // Log errors to wp-content/debug.log define( 'WP_DEBUG_DISPLAY', false ); // Do not display errors on the public site @ini_set( 'display_errors', 0 ); // Ensure errors aren't displayed - Save the `wp-config.php` file.
- Reproduce the issue you were experiencing with the WP Optimal State plugin.
- Check the `wp-content/debug.log` file via FTP/File Manager. It may contain specific PHP errors or warnings related to the problem.
- Important: Once you have finished troubleshooting, remember to change `WP_DEBUG` back to `false` in `wp-config.php` to avoid logging errors on a live site. You can leave `WP_DEBUG_LOG` and `WP_DEBUG_DISPLAY` as they are, or remove them.
Note: Never leave `WP_DEBUG` set to `true` or `WP_DEBUG_DISPLAY` set to `true` on a live production website, as it can expose sensitive information.
Best Practices
Maintenance Schedule
Establish a routine for database maintenance. Adjust frequency based on site activity.
Using the Automated Scheduler (Recommended)
- Set & Forget: Configure the scheduler (Section 7) based on your site type (see recommendations there, e.g., weekly for blogs, monthly for business sites).
- Enable Email Notifications: Receive confirmation or failure reports.
- Monitor Logs/Backups: Periodically check that automated backups are being created and review the Optimization Log.
Manual Maintenance Routine (If Not Using Scheduler)
Weekly (5-10 mins):
- Create Backup (Section 1).
- Run One-Click Optimization (Section 2).
- Review Statistics & Health Score (Sections 3 & 4).
Monthly (15-30 mins):
- Create & Download Backup (Section 1).
- Run safe individual cleanups (Revisions, Drafts, Spam, Orphans, Expired Transients) (Section 5).
- Run “Optimize Autoloaded Options” (Section 6).
- Run “Optimize All Tables” (Section 6).
- Review site functionality.
Quarterly/Annually (30-60 mins):
- Create & Download Backup.
- Perform Monthly tasks.
- Run “Analyze & Repair Tables” (Section 6).
- Clean Duplicate Metadata (Section 5).
- Review Trashed Posts/Unapproved Comments and clean if appropriate (Section 5).
- Review Performance Features settings (Section 8).
- Consider testing backup restoration on a staging site.
Performance Optimization Tips
Combine WP Optimal State with other best practices for maximum performance.
Database-Level Optimization (Using WP Optimal State)
- Control Revisions: Use the Performance Features Manager (Section 8) to limit revisions (e.g., to 5 or 10) instead of letting them grow infinitely.
- Regular Cleanup: Use the scheduler or manual routines to consistently remove revisions, drafts, spam, orphans, and expired transients.
- Manage Autoload: Run “Optimize Autoloaded Options” periodically, especially after adding/removing plugins. Monitor the autoload size statistic.
- Optimize Tables Regularly: Include “Optimize All Tables” in your routine, especially after large data deletions.
- Monitor Health: Use the Health Score and Statistics to identify areas needing attention.
WordPress-Level Optimization (Beyond WP Optimal State)
- Caching: Implement page caching. You can use WP Optimal State’s built-in Server-Side Page Caching feature (see Performance Features Manager) for a simple and effective solution, or a dedicated third-party plugin (e.g., WP Rocket, W3 Total Cache, host-level cache). Do not use both simultaneously. Consider object caching (Redis/Memcached) for further database query reduction.
- Image Optimization: Compress images before uploading and use plugins (e.g., Smush, ShortPixel) to optimize existing ones. Use modern formats like WebP.
- Plugin/Theme Audit: Regularly review and remove unused plugins and themes. Choose well-coded, performant options.
- CDN (Content Delivery Network): Use a CDN (e.g., Cloudflare, BunnyCDN) to serve static assets (images, CSS, JS) from servers closer to visitors, reducing load on your server.
- Minimize External Requests: Reduce the number of external scripts, fonts, and API calls loaded on your pages.
- Code Optimization: Ensure custom code in themes/plugins is efficient and avoids slow database queries. Use tools like Query Monitor for analysis.
Server-Level Optimization
- Use Latest PHP Version: Update to a recent, stable PHP version (e.g., 8.0+) for significant performance gains.
- Sufficient Resources: Ensure your hosting plan provides adequate RAM, CPU, and SSD storage.
- Database Server Tuning: Consult with your host about optimizing MySQL/MariaDB configuration (buffer sizes, caches).
- Enable Gzip/Brotli Compression: Configure your web server (Apache/Nginx) to compress text-based assets.
- HTTP/2 or HTTP/3: Ensure your server supports modern HTTP protocols for faster asset loading.
Security Best Practices
While WP Optimal State includes security measures, follow general WordPress security practices.
Using WP Optimal State Securely
- Always Backup First: Before any cleanup, optimization, restore, or performance feature change. Download backups periodically.
- Use Staging Environment: Test significant changes (especially restores or disabling core features) on a non-production site first.
- Limit Access: Only Administrator roles can access the plugin. Avoid sharing admin credentials.
- Understand Operations: Know what each button does before clicking, especially those with warnings (⚠️).
- Keep Updated: Update WP Optimal State, WordPress, PHP, themes, and other plugins promptly.
- Monitor Activity: Review scheduled task outcomes (via email or logs if configured).
General WordPress Security
- Use strong, unique passwords for all accounts.
- Implement two-factor authentication (2FA).
- Install a reputable security plugin (e.g., Wordfence, Sucuri Security).
- Keep everything updated (Core, Themes, Plugins).
- Choose reputable hosting with security features.
- Limit login attempts.
- Use SSL/HTTPS.
- Regularly scan for malware.
- Disable file editing in the dashboard (`define(‘DISALLOW_FILE_EDIT’, true);` in `wp-config.php`).
Backup Strategy
Reinforce the importance of backups mentioned earlier.
3-2-1 Rule: 3 copies, 2 different media types, 1 offsite.
Frequency: Daily or more frequent for active sites. Use WP Optimal State backups + hosting backups + offsite backups.
Testing: Regularly test restoring backups to ensure they work.
Content Management Guidelines
How content practices affect the database and WP Optimal State usage.
Post Revisions
- Limit Them: Use the Performance Features Manager (Section 8) or `wp-config.php` (`define(‘WP_POST_REVISIONS’, 5);`) to prevent excessive buildup.
- Clean Regularly: Include revision cleanup in your routine maintenance.
Comments
- Moderate Promptly: Approve or trash pending comments regularly.
- Use Anti-Spam: Tools like Akismet are essential to prevent spam buildup.
- Clean Regularly: Include Spam and Trashed Comments cleanup in your routine. Consider cleaning Unapproved Comments periodically after review.
- Disable Comments/Pingbacks: If not needed site-wide or on older posts, disable them in WordPress settings (Settings -> Discussion).
Media Management
While WP Optimal State doesn’t manage files, excessive media metadata can contribute to database size.
- Clean Up Unused Media: Periodically use plugins designed to find and remove media files not attached to any posts/pages. Deleting the media file often removes associated metadata.
- Optimize Images: Smaller images mean faster loading, though this doesn’t directly impact database size significantly (metadata size is usually small).
Plugin/Theme Usage
- Remove Unused Items: Deactivated plugins/themes can still leave data (options, tables) in the database. Properly uninstall them (look for uninstall routines) and consider manually removing leftover tables (use Database Structure Analysis for identification, requires tools like phpMyAdmin for removal – backup first!).
- Choose Wisely: Select plugins/themes known for being well-coded and efficient to minimize database bloat from the start.
How to Update
Your update process depends on whether you are using the FREE or PRO version. Please read the correct section for your plugin.
✔ UPDATING THE FREE VERSION
If you installed the free version of WP Optimal State from the official WordPress plugin repository, you can update it directly from your WordPress dashboard.
- Go to Plugins → Installed Plugins.
- Find WP Optimal State and click the “update now” link.
✅ All your database backups and settings will be preserved automatically.
⭐ UPDATING THE PRO VERSION
Updating the PRO version (which you received as a .zip file) takes just a couple of minutes. You have two equally valid options.
💡 Option 1: Via the Dashboard
- In the plugin interface, go to section 1 and download your database backups (they will download as compressed
.sql.gzfiles). - Then, go to section 9 (Settings Export & Import) and click Export Settings to download your
.jsonsettings file. - Go to Plugins > Add Plugin, then click Upload Plugin. Choose the
.zipfile containing the latest plugin release and click Install Now. - At this point, you will now be asked to either replace the current version with the uploaded one, or cancel and go back. Click Replace current with uploaded.
- The update is complete! Visit the plugin admin panel to confirm that your backups and settings are intact.
👨💻 Option 2: Via FTP Client
- Unzip the new plugin
.zipfile on your computer to get a folder namedoptistate. - Open your FTP client or hosting file explorer and navigate to
wp-content/plugins/. - Upload the
optistatefolder from your computer, choosing to replace or overwrite all existing files in the/wp-content/plugins/optistate/directory. - Once complete, go to Plugins > Installed Plugins, find WP Optimal State and verify that the new version number is displayed.
- The update is complete! Visit the plugin admin panel to confirm that your backups and settings are intact.
📥 How to Get PRO Updates
- You will receive an email notification when a new version is released.
- Download the update from your account on the purchase site (Payhip.com).
- If you did not register at the time of purchase or no longer have access to your account, contact 🆘 Technical Support with your license key and website URL. We will send the update package to you via email.
FAQ
General Questions
Is there a DEMO version available?
We have something even better than a demo for you to enjoy: The FREE version of WP Optimal State! Download it free of charge, try it out and then decide whether to purchase the PRO version. Simply select “FREE Version” and then proceed to checkout. No credit card needed!
What’s the difference between the FREE and PRO versions?
The FREE version includes basic optimization features like cleaning post revisions, spam comments, and expired transients. The PRO version adds advanced features including automated scheduling, extended backup management, autoload optimization, database repair tools, comprehensive caching options, and priority support. Try the FREE version first to experience the core functionality.
How do I upgrade from FREE to PRO version?
The upgrade process is straightforward. Simply replace the free version with the PRO version.
👉 Follow these quick steps:
- In the plugin interface, go to section 1 and download your database backups (they will download as compressed
.sql.gzfiles). - Then, go to section 9 (Settings Export & Import) and click Export Settings to download your
.jsonsettings file. - Go to Plugins > Add Plugin, then click Upload Plugin. Choose the zip file
WP_Optimal_State_PRO_X-X-X.zipcontaining the PRO version and click Install Now. - At this point, you will now be asked to either replace the current version with the uploaded one, or cancel and go back. Click Replace current with uploaded.
- The update is complete! Visit the plugin admin panel to confirm that your backups and settings are intact.
- If your settings have not been properly preserved, go to section 9 and import the
.jsonfile you downloaded in step 2.
*IMPORTANT: If buttons in the admin interface are not working after upgrading, perform a hard refresh of your browser:
Ctrl+F5 on Windows/Linux – Cmd+Shift+R on Mac).
If you don’t feel confident enough, please purchase PRO Version + Installation and we’ll handle everything for you.
How do I install plugin updates?
The update procedure needs to be performed manually by choosing one of the two available methods. These steps are simple and take just a few minutes, requiring minimal technical knowledge. See section 2.7 of the user manual for details: 2.7. Keep the Plugin Updated.
If you are using the free version, we recommend installing it via the official WordPress plugin repository. This will allow you to update the plugin directly from your dashboard. To install it via the repository, in your dashboard go to Plugins > Add Plugin > Search Plugins > Search for “Optimal State” > Install Now & Activate.
Is WP Optimal State safe to use?
Yes, when used correctly and cautiously.
Always create a backup before any operation (especially cleanup, restore, or changing performance features). Start with low-risk operations like “One-Click Optimization” or cleaning expired transients/spam. Understand what operations marked with ⚠️ do before running them. Test on a staging site if possible.
My website is hosted on an Nginx server: Will the plugin still work?
Yes, but with some limitations that can be fixed manually if you possess some technical knowledge.
The security of several directories created by WP Optimal State relies on placing specific rules in the .htaccess file, which is not found on Nginx servers. Similarly, the Browser Caching feature will not work automatically as it requires the existence of the .htaccess file. Refer to Section 7.3.1 of the user manual for instructions on how to overcome these restrictions and access the plugin’s full functionality.
What makes WP Optimal State different from other database optimization plugins?
WP Optimal State combines database cleanup, performance optimization, and backup management in a single interface. It features intelligent safety mechanisms including automated backup creation, operation warnings, exclusion lists for critical data, and a safe restore process with atomic table swapping. The plugin provides detailed statistics before operations and maintains optimization logs for transparency.
Performance & Results
Will this plugin significantly speed up my website’s front-end?
It primarily improves backend performance (admin dashboard speed, query times) and reduces database size. Front-end speed improvements are often secondary and depend on how database-intensive your theme/plugins are. You might see a modest front-end speed boost (e.g., 5-15%), but major front-end gains usually require caching, image optimization, and code optimization. WP Optimal State complements these efforts by ensuring the database itself is efficient.
How much database space can I realistically expect to save?
This varies greatly depending on site age, content volume, plugin usage, and past maintenance:
- Sites with many post revisions or years of accumulated spam/transients can see significant reductions (20-50%+).
- Well-maintained or newer sites might see smaller reductions (5-15%).
- The biggest savings usually come from cleaning revisions, spam, transients, and optimizing table overhead.
Focus on improved performance and efficiency rather than just size reduction.
My statistics show 0 for many items, but the database size is still large. Why?
A large database size doesn’t necessarily mean there’s lots of cleanable junk. The size includes:
- Your actual content: Posts, pages, comments, users, media library entries (metadata), etc. WP Optimal State won’t (and shouldn’t) delete this.
- Data stored by plugins and themes in standard tables (e.g., WooCommerce orders in
wp_postsandwp_postmeta) or their own custom tables. - Table structure overhead and index sizes.
- Internal fragmentation within table files (especially InnoDB).
Focus on optimizing what can be cleaned (revisions, spam, transients, overhead) and use the Database Structure Analysis tool to identify unexpectedly large tables that might need further investigation (e.g., logs stored by a plugin).
I ran a cleanup, it said items were deleted, but the database size didn’t change?
This is common, especially with the InnoDB storage engine.
Run “Optimize All Tables” after cleaning. This encourages the database to reclaim space. Even after optimization, InnoDB might not shrink the physical .ibd file on disk. It reuses the freed space internally for future data. The usable space has increased, even if the file size hasn’t dropped. The amount of data deleted might have been small relative to the total database size.
Usage & Best Practices
How often should I run the optimizations?
Use the Automated Scheduler for consistency. Recommended manual frequencies:
- Weekly: One-Click Optimization (or equivalent safe cleanups + Optimize Tables).
- Monthly: More thorough cleanup including Autoload Optimization and Analyze/Repair Tables.
- As Needed: After major content changes, plugin removals, or if performance degrades.
Adjust based on your site’s activity and hosting environment.
What’s the safest way to use WP Optimal State for the first time?
Start with these steps:
- Create a database backup using the plugin or your hosting panel.
- Download the backup file to your computer.
- Review the statistics to understand what will be cleaned.
- Start with “One-Click Optimization” which targets only safe, non-critical data.
- Monitor your site functionality immediately after.
- Gradually explore individual cleanup operations once comfortable.
If you have a staging site, test there first before running on production.
Should I run operations during peak traffic times?
No. Always run database operations during low-traffic periods. Intensive operations like backups, restores, or table optimization can temporarily slow down your site or lock tables. Schedule automated operations for off-peak hours (typically late night/early morning in your timezone).
Safety & Data Management
Can I undo a cleanup operation if I make a mistake?
No, cleanup operations permanently delete data directly from the database (they don’t use a trash bin). The only way to undo a cleanup is by restoring a database backup created before the cleanup was performed. This emphasizes the critical importance of backups.
Will cleaning operations affect my published posts, pages, or user comments?
Safe operations (those without a ⚠️ warning) are designed not to affect your live, published content. They target:
- Old versions (revisions)
- Content already in the trash (posts/comments)
- Spam comments
- Data related to deleted items (orphans)
- Temporary cache data (transients)
- Redundant data (duplicates)
Operations like “Clean Trashed Posts” or “Clean Unapproved Comments” do permanently delete that specific content, hence the warnings.
What exactly happens to the data when it’s “cleaned” or “deleted”?
The plugin executes standard SQL DELETE commands. This permanently removes the specified rows from the database tables. The data is not moved to a separate trash or recoverable within the plugin itself. Recovery is only possible by restoring a database backup.
Can I get back data accidentally deleted by the plugin?
Only if you have a database backup created before the deletion occurred. Restore that backup. There is no “undo” button within the plugin.
Will this plugin delete my images or other media files?
No. WP Optimal State operates ONLY on the WordPress database. It does not interact with, modify, or delete any files in your wp-content/uploads directory (where images and media are stored) or any other theme/plugin files.
Backup & Restore
How do I restore a backup created by WP Optimal State?
Go to Section 1.1 (“Manage Existing Backups”), find the backup file in the list, click the “Restore” button next to it, and confirm the action in the pop-up modal. Ensure you select the correct backup. The plugin handles the verification and safe restore process.
Where are backups stored and can I download them?
Backups are stored in the wp-content/uploads/optistate/ directory on your server. You can download them directly from the plugin’s backup management interface. Always keep downloaded copies of important backups on your local computer or cloud storage as an additional safety measure.
How long does a backup or restore take?
This depends entirely on your database size and server resources. Small databases (under 100MB) typically take seconds to a few minutes. Larger databases (300MB+) can take 10 minutes or more. If you experience timeouts, increase your server’s max_execution_time setting.
Can I schedule automatic cleanups and backups?
Yes. Section 7 (“Automatic Backup and Cleanup”) allows you to set a daily frequency (1-365 days) and a specific hour for the plugin to automatically create a backup and run the One-Click Optimization routine. You can also enable email notifications for these tasks.
Specific Features & Operations
What’s the difference between cleaning “Expired Transients” and “All Transients”?
Expired Transients: Deletes only temporary cache entries whose designated expiration time has passed. This is generally safe and recommended for regular maintenance.
All Transients: Deletes ALL transient entries, regardless of whether they have expired. This forces regeneration of all transient caches and can temporarily slow down your site. Use this mainly for troubleshooting caching issues.
Will “Optimize Autoloaded Options” delete important settings for my theme or plugins?
It’s designed not to. The plugin maintains an internal exclusion list of common critical option names (core WordPress settings, popular plugin prefixes like WooCommerce, Yoast, Elementor, etc.). It avoids changing the autoload flag for these options, even if they are large. While it’s impossible to list every possible plugin option, the risk of breaking essential functionality is low. However, poorly coded plugins relying on large autoloaded data might be affected. Backup first if concerned.
Why won’t the Autoloaded Options Size decrease after running the optimization?
Possible reasons:
- The largest options might be on the exclusion list (essential core/plugin settings).
- Plugins might immediately regenerate the large options that were just set to
autoload = 'no'. This indicates a potentially inefficient plugin that should be investigated or replaced. - The total size of optimizable large options was small to begin with.
- Caching might delay the statistic update (try refreshing stats).
Check the details provided after running the optimization to see which options were targeted and which were skipped.
Does the plugin clean data related to custom post types (CPTs) and custom taxonomies?
Yes. Cleanup operations targeting standard WordPress tables work universally:
- Revisions for CPTs are stored in
wp_posts(post_type = 'revision') and are cleaned. - Metadata for CPTs (custom fields) is stored in
wp_postmetaand orphaned CPT meta is cleaned. - Relationships between CPTs and custom taxonomies are stored in
wp_term_relationships, and orphaned relationships are cleaned. - Trashed CPTs are stored in
wp_posts(post_status = 'trash') and are cleaned by “Clean Trashed Posts”.
Does the plugin keep a detailed log of every single item deleted?
The main results display shows the count of items deleted per category immediately after an operation. A persistent Optimization Log (stored in wp-content/uploads/optistate-settings/optimization-log.json) records the type of operation performed (e.g., “One-Click Optimization”, “Database Backup Created”), the timestamp, and the number of items affected if applicable, but not the specific IDs of every deleted row. For granular, row-level logging, you would need more advanced database auditing tools, which is beyond the scope of this plugin.
Compatibility & Technical
Is WP Optimal State compatible with WooCommerce?
Yes, the plugin’s operations work on the standard WordPress database structure that WooCommerce utilizes. Cleaning transients, optimizing tables, and managing backups function correctly with WooCommerce installed. The “Optimize Autoloaded Options” feature includes exclusions for common WooCommerce options.
Is this plugin compatible with multisite?
No, WP Optimal State is designed for single-site WordPress installations only. It does not correctly handle the table structures (wp_1_posts, wp_2_options, etc.) used in a multisite network and should not be used on multisite installs.
Does this work on managed WordPress hosting (e.g., WP Engine, Kinsta, Flywheel)?
Generally yes, as it uses standard WordPress functions and SQL commands. However:
- Managed hosts often have their own robust caching layers; cleaning transients might have less impact or conflict if object caching (Redis/Memcached) is heavily managed by the host.
- Some hosts might restrict direct database optimization commands (
OPTIMIZE TABLE,REPAIR TABLE) or have specific recommendations/tools for database maintenance. - Aggressive Heartbeat API control might interfere with host-specific monitoring or features.
Check your hosting provider’s documentation or support regarding database optimization plugins.
Could WP Optimal State conflict with caching plugins (WP Rocket, W3TC, etc.) or object cache (Redis/Memcached)?
Yes, a conflict WILL occur if you enable WP Optimal State’s built-in Server-Side Page Caching or Browser Caching (.htaccess) features while another caching plugin (like WP Rocket, LiteSpeed Cache, W3 Total Cache, etc.) is active.
Page Caching: You must choose one. DO NOT run two page caching systems simultaneously as this will cause conflicts.
Database Cleanup: The database cleanup features (like cleaning Transients, Post Revisions, etc.) are generally safe to use alongside other caching plugins. Cleaning transients may simply cause your other plugin to rebuild its cache, which is normal.
Object Cache: The plugin is compatible with object cache solutions like Redis or Memcached.
Does the plugin add its own tables to my database?
No, WP Optimal State does not create any permanent custom database tables for its own settings or logs. Settings and logs are stored as JSON files in the wp-content/uploads/optistate-settings/ directory. Temporary tables (optistate_temp_…, optistate_old_…) are created only during the database restore process and are automatically cleaned up afterward.
What specific MySQL/MariaDB database user permissions are needed?
The plugin requires the standard permissions typically granted to the WordPress database user during installation. These generally include:
SELECT: To read data for statistics and cleanup checks.INSERT,UPDATE,DELETE: To perform cleanup operations.CREATE,DROP,ALTER,RENAME: For table optimization, repair, and the temporary table swapping during restores.REFERENCES,INDEX: Often needed for table operations.
If you encounter permission errors, verify the grants for the user defined in wp-config.php.
Troubleshooting
My site seems slower right after cleaning “All Transients”. Is it broken?
No, this is usually expected and temporary. Cleaning “All Transients” removes active caches, forcing WordPress and plugins to regenerate them. This requires extra processing and database queries initially, causing a temporary slowdown. Performance should return to normal (or improve) as caches rebuild naturally through site usage. Avoid cleaning “All Transients” unless troubleshooting specific caching issues; use “Expired Transients” for routine maintenance.
I’m getting “Out of Memory” errors during operations. What should I do?
The operation requires more RAM than your server’s PHP configuration allows.
Increase the PHP memory_limit. Contact your hosting provider or try setting it via wp-config.php (e.g., define('WP_MEMORY_LIMIT', '256M');), .htaccess, or php.ini / MultiPHP INI Editor in cPanel. Start with 256M or 512M.
For cleanups, process fewer items at once (clean individually instead of One-Click). For backups/restores on very large sites, consider server-level tools (mysqldump) or specialized backup plugins designed for large sites.
Operations are timing out (e.g., backup, restore, optimize). How can I fix this?
The operation takes longer than the server’s maximum script execution time.
Increase the PHP max_execution_time. Contact your hosting provider or try setting it via wp-config.php (e.g., @ini_set('max_execution_time', '300'); for 5 minutes), .htaccess, or php.ini.
Run operations during low-traffic periods when the server is less busy. For cleanups, process fewer items at once. Use WP-CLI for potentially faster execution without web server timeouts.
I activated the plugin, but the “Optimal State” menu item doesn’t appear, or the page is blank/errors out.
Possible causes:
- Permissions: Ensure you are logged in as an Administrator.
- PHP Version: Double-check your server is running PHP 7.4 or higher. Older versions will cause fatal errors.
- Plugin Conflict: Temporarily deactivate all other plugins and switch to a default theme (like Twenty Twenty-Three) to see if the menu appears. If it does, reactivate plugins one by one to find the conflict.
- Incomplete Installation: Try deactivating, deleting, and reinstalling the plugin.
- File Permissions: Less likely, but server file permission issues could prevent plugin files from loading.
- Check Error Logs: Enable WP_DEBUG or check server PHP error logs for specific fatal errors.
Advanced Usage
What’s the practical limit on database size for this plugin? Can it handle 1GB+ databases?
There’s no hardcoded limit. However, performance depends heavily on server resources (CPU, RAM, disk I/O) and configuration (PHP timeouts, memory limits, MySQL tuning).
Large Databases (e.g., 1GB+): Operations like backups, restores, table optimization, and scanning for orphans/duplicates will take significantly longer and are more likely to hit server timeouts or memory limits.
Recommendations for Large DBs:
- Ensure high
max_execution_timeandmemory_limit. - Run operations during very low traffic periods.
- Consider using WP-CLI for optimization tasks if web-based operations time out.
- Backup/Restore might be more reliably handled by server-level tools (like
mysqldumpcommand line or hosting panel backups) for very large databases, although WP Optimal State’s restore includes safety features like the atomic swap.
Is it truly safe to use this on a live production site?
Yes, if you follow safety precautions:
- Backup First: Non-negotiable. Ensure you have a recent, downloadable backup.
- Understand Actions: Know what each cleanup/optimization does, especially those with warnings (⚠️).
- Use Staging First (Ideally): Test on a copy of your site if possible.
- Low Traffic Times: Run operations when site activity is minimal.
- Monitor After: Check site functionality immediately after operations.
The plugin is designed with safety features (exclusions, safe restore process), but direct database operations always carry inherent risks if precautions are ignored.
Can I use WP Optimal State via WP-CLI?
While the plugin is primarily designed for use through the WordPress admin interface, its database operations use standard WordPress functions that can be adapted for WP-CLI usage. For very large databases experiencing timeout issues, WP-CLI can provide more reliable execution. Check with support for specific WP-CLI integration guidance.
Technical Information
System Requirements
What are the minimum system requirements?
- WordPress: 5.5 or higher
- PHP: 7.4 or higher
- MySQL: 5.6+ / MariaDB 10.0+
- Memory: 128MB PHP
memory_limit - User Role: Administrator
- File System: Writable
wp-content/uploads/(specifically needs to createoptistateandoptistate-settingssubdirectories)
What are the recommended system requirements for optimal performance?
- WordPress: Latest Version
- PHP: 8.2 or higher
- MySQL: 5.7+ / MariaDB 10.3+
- Memory: 256MB+ PHP
memory_limit - Storage: SSD Hosting
- Execution Time:
max_execution_timeof 60+ seconds (higher for large DBs)
Database Operations
Tables Modified by Cleanup
The plugin primarily interacts with standard WordPress core tables using `DELETE` and `UPDATE` (for autoload optimization) queries.
| Table Name (Default Prefix) | Relevant Cleanup Operations |
|---|---|
| `wp_posts` | Clean Post Revisions, Clean Auto Drafts, Clean Trashed Posts |
| `wp_postmeta` | Clean Orphaned Post Meta, Clean Duplicate Post Meta |
| `wp_comments` | Clean Spam Comments, Clean Trashed Comments, Clean Unapproved Comments, Clean Pingbacks, Clean Trackbacks |
| `wp_commentmeta` | Clean Orphaned Comment Meta, Clean Duplicate Comment Meta |
| `wp_usermeta` | Clean Orphaned User Meta |
| `wp_term_relationships` | Clean Orphaned Relationships |
| `wp_options` | Clean Expired Transients, Clean All Transients, Optimize Autoloaded Options |
All Tables: Affected by `OPTIMIZE TABLE` and `CHECK TABLE`/`REPAIR TABLE` operations. The restore process (`RENAME TABLE`, `DROP TABLE`) also affects all tables included in the backup.
SQL Queries Used (Conceptual Examples)
The plugin uses WordPress Database API (`$wpdb`) methods which generate SQL similar to this:
-- Get stats (simplified)
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM `wp_posts` WHERE `post_type` = 'revision';
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM `wp_comments` WHERE `comment_approved` = 'spam';
SELECT COUNT(pm.meta_id) FROM `wp_postmeta` pm LEFT JOIN `wp_posts` p ON pm.post_id = p.ID WHERE p.ID IS NULL;
SELECT SUM(LENGTH(option_value)) FROM `wp_options` WHERE `autoload` = 'yes';
SELECT SUM(data_free) FROM information_schema.TABLES WHERE table_schema = DATABASE();
-- Perform cleanups (simplified)
DELETE FROM `wp_posts` WHERE `post_type` = 'revision';
DELETE FROM `wp_comments` WHERE `comment_approved` = 'spam';
DELETE pm FROM `wp_postmeta` pm LEFT JOIN `wp_posts` p ON pm.post_id = p.ID WHERE p.ID IS NULL;
DELETE FROM `wp_options` WHERE `option_name` LIKE '_transient_timeout_%' AND `option_value` < UNIX_TIMESTAMP();
DELETE FROM `wp_postmeta` WHERE `meta_id` IN (SELECT meta_id FROM ... subquery identifying duplicates ...);
-- Optimize / Repair
OPTIMIZE TABLE `wp_posts`;
CHECK TABLE `wp_comments`;
REPAIR TABLE `wp_options`; -- (If CHECK finds errors)
-- Autoload Optimization
UPDATE `wp_options` SET `autoload` = 'no' WHERE `option_name` = 'some_large_option_name' AND `autoload` = 'yes';
-- Restore (Conceptual - involves many queries and RENAME)
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `optistate_temp_wp_posts`;
CREATE TABLE `optistate_temp_wp_posts` (...);
INSERT INTO `optistate_temp_wp_posts` VALUES (...); -- Data from backup
-- ... repeat for all tables ...
START TRANSACTION;
RENAME TABLE `wp_posts` TO `optistate_old_wp_posts`;
RENAME TABLE `optistate_temp_wp_posts` TO `wp_posts`;
-- ... repeat for all tables ...
COMMIT;
DROP TABLE `optistate_old_wp_posts`;
-- ... repeat for all old tables ...
Performance Impact
During Operation
Resource usage varies significantly based on the operation and database size.
- CPU: Can be high during large `DELETE` queries, table optimization/repair, backups, and restores. Short bursts for statistics gathering.
- Memory (PHP): Fetching large datasets (e.g., checking duplicates, analyzing autoload) can consume memory. Backups/restores processing SQL files also use memory.
- Disk I/O: High during backups (writing `.sql` file), restores (reading `.sql` file, writing to temp tables, renaming), and table optimization/repair (reading/writing table data).
- Database Load: Queries for stats are generally light. `DELETE` queries can be intensive. `OPTIMIZE`/`REPAIR`/`RENAME` can lock tables, potentially blocking other site operations temporarily.
Site Impact: Generally minimal for visitors during quick cleanups or stats checks. Longer operations (backup, restore, full optimize/repair on large DBs) can cause noticeable backend slowdown or brief frontend unresponsiveness due to table locks or server load. Restores activate maintenance mode for visitors.
After Operation (Potential Benefits)
- Reduced database size (less disk space, faster backups).
- Faster database queries (due to smaller tables, optimized indexes, less overhead).
- More responsive WordPress admin area.
- Reduced server memory usage (if large autoloaded options were optimized).
- Improved database stability (if tables were repaired).
Security Features
The plugin incorporates several security practices:
- Nonce Verification: All actions triggered via AJAX (buttons, saving settings) use WordPress nonces to prevent Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) attacks.
- Capability Checks: Access to the plugin page and execution of all actions are restricted to users with the `manage_options` capability (typically Administrators only). Specific actions like backup/restore also check relevant capabilities (`export`, `import`).
- Input Sanitization: Data received from user input (e.g., settings values, filenames) is sanitized using functions like `absint()`, `sanitize_text_field()`, `sanitize_file_name()`, `sanitize_key()`.
- Output Escaping: Data displayed on the admin page (e.g., statistics, filenames, messages) is escaped using functions like `esc_html()`, `esc_attr()`, `esc_url()` to prevent Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attacks.
- Database Query Preparation: Where applicable, `$wpdb->prepare()` is used to prevent SQL injection vulnerabilities, especially with dynamic table or column names (though most queries target fixed structures). Table name validation (`validate_table_name`) is used before dynamic table operations.
- Filesystem Abstraction: Uses `WP_Filesystem` for file operations (creating directories, writing/reading settings/logs, managing backups), which handles credentials and permissions more securely than direct PHP file functions.
- Path Validation: File operations include checks (`validate_file_path`) to prevent directory traversal attacks (e.g., ensuring backups are only written/read within the designated backup directory).
- Backup/Restore Security:
- Backup directory protected via `.htaccess` and `index.php`.
- Backup integrity checked via SHA-256 checksums before restore and download.
- Uploaded restore files undergo security checks (type, size, content sniffing, path validation).
- Temporary restore files stored in a separate, protected directory with restricted permissions.
- Rate Limiting: Some potentially intensive actions (backup creation, restore) have basic time-based rate limiting using transients to prevent abuse.
Compatibility
WordPress Versions
- Minimum Declared: 5.5
- Tested up to: 6.8.3
PHP Versions
- Minimum Declared: 7.4
- Recommended: 8.0+
Database Systems
- MySQL 5.6+
- MariaDB 10.0+
Plugin/Theme Compatibility
Generally compatible with most themes and plugins as it primarily interacts with standard WP core tables and functions. Potential areas for conflict (rare):
- Plugins aggressively manipulating WP Cron schedules.
- Plugins heavily modifying database query behavior.
- Security plugins overly strict on AJAX actions or file operations (might need configuration).
- Other database cleanup plugins running simultaneously.
Known Incompatibilities
- WordPress Multisite: Not designed for or tested with Multisite. Use on single-site installs only.
File Structure
[plugin-install-directory]/ (e.g., wp-content/plugins/optistate/)
├── optistate.php # Main plugin file (includes OPTISTATE and OPTISTATE_Backup_Manager classes)
├── css/
│ └── admin.css # Styles for the admin dashboard page
├── js/
│ └── admin.js # JavaScript for AJAX calls, UI interactions (modals, toggles)
├── languages/
│ └── optistate.pot # Translation template file
├── images/
│ └── optistate-logo-small.webp # Logo displayed
on admin page
├── readme.txt # Standard WordPress plugin readme file
└── LICENSE.txt # Copy of the GPL v2 license (Assumed)
Data Storage Location (within wp-content/uploads/):
├── optistate-settings/
│ ├── settings.json # Stores plugin settings (schedule, max backups, performance features)
│ └── optimization-log.json # Log of cleanup/backup/restore operations
│ └── .htaccess # Protects files from direct web access
├── optistate/
│
├── db-backups/ # Stores .sql.gz database backup files
│ │ ├── DB-BACKUP-....sql.gz
│ │ ├── DB-BACKUP-....sql.gz.checksum # SHA-256 checksum file
│ │ └── DB-BACKUP-....sql.gz.meta # Metadata JSON file
│ │ └── .htaccess # Protects files from direct web access
│ │ └── index.php # Prevents directory listing
│ ├── db-restore-temp/
# Temporarily stores uploaded .sql files for restore
│ │ └── .htaccess # Protects files from direct web access
│ │ └── index.php # Prevents directory listing
│ └── page-cache/ # Stores static HTML files for Server-Side Page Caching
│ ├── ... (cache files) ...
│ └── .htaccess # Protects files from direct web access
│ └── index.php # Prevents directory listing
Hooks & Filters
Actions Used/Triggered
- Plugin Activation/Deactivation: Uses `register_activation_hook`, `register_deactivation_hook` for setup (creating directories, scheduling cron) and cleanup (unscheduling cron, removing .htaccess rules).
- Plugin Load: Uses `muplugins_loaded` (for early cache check) and `init` (for general setup, cron scheduling, and download handling).
- Admin Menu: Uses `admin_menu` to add the “Optimal State” menu item.
- Admin Assets: Uses `admin_enqueue_scripts` to load `admin.css` and `admin.js` on the plugin page.
- AJAX Handlers: Uses `wp_ajax_optistate_*` actions to handle button clicks and data requests (e.g., `wp_ajax_optistate_get_stats`, `wp_ajax_optistate_create_backup`, `wp_ajax_optistate_purge_page_cache`).
- WP Cron: Schedules and uses custom cron hooks:
- `optistate_scheduled_cleanup`: For the main automated backup & cleanup task.
- `optistate_daily_cleanup`: For internal tasks like cleaning old temporary restore files (runs hourly despite name).
- Admin Notices: Uses `admin_notices` to display warnings (e.g., permission issues).
- Performance Features: Hooks into various core actions/filters depending on the enabled feature (e.g., `heartbeat_settings`, `xmlrpc_enabled`, `wp_head`, `pre_ping`).
- Cache Purging: Hooks into WordPress content actions to automatically purge cache:
- `transition_post_status`
- `post_updated`
- `transition_comment_status`
- `edited_term`
- Restore Process: Uses `template_redirect` to show maintenance page during restore.
Filters Used
Primarily uses filters related to the Performance Features Manager when those options are active (e.g., `heartbeat_settings`, `xmlrpc_enabled`, `emoji_svg_url`, `the_generator`). Does not add significant custom filters for external modification.
WP-CLI Usage (Advanced)
While WP Optimal State doesn’t add its own specific WP-CLI commands, you can use built-in WP-CLI commands that achieve similar results for some tasks, especially useful for very large databases or automation scripts:
# Optimize all database tables
wp db optimize
# Repair all database tables
wp db repair
# Check database tables
wp db check
# Clean expired transients
wp transient delete --expired
# Clean ALL transients (Use with caution!)
wp transient delete --all
# Export database (similar to backup)
wp db export my_backup_filename.sql.gz
# Import database (similar to restore - USE EXTREME CAUTION!)
# wp db import my_backup_filename.sql.gz
# Delete post revisions (requires looping or custom script)
# Example: Delete revisions older than 30 days (careful!)
# wp post delete $(wp post list --post_type='revision' --field=ID --post_date_before=$(date -d '30 days ago' +%Y-%m-%d)) --force
# Delete spam comments
wp comment delete $(wp comment list --status=spam --format=ids) --force
# Delete trashed comments
wp comment delete $(wp comment list --status=trash --format=ids) --force
# Delete trashed posts
wp post delete $(wp post list --post_status=trash --format=ids) --force
Note: WP-CLI commands operate directly and bypass plugin-specific logic (like safety checks, logging, or UI feedback). Always backup before using WP-CLI for destructive operations.
Advanced Configuration
Most settings are managed via the plugin interface. Advanced server/WordPress configurations can influence plugin behavior:
PHP Configuration (`php.ini`, `.htaccess`, `wp-config.php`)
- `max_execution_time`: Affects how long operations can run before timing out. Increase for large databases (e.g., 300+ seconds).
- `memory_limit`: Affects how much data can be processed at once. Increase for large databases (e.g., 256M+).
- `upload_max_filesize`, `post_max_size`: Affect the ability to upload large backup files for restore.
WordPress Configuration (`wp-config.php`)
- `WP_POST_REVISIONS`: Can conflict with the plugin’s Performance Feature setting for revisions if both are set. The `wp-config.php` definition usually takes precedence.
- `DISABLE_WP_CRON`: If set to `true`, the Automated Scheduler will not run unless a server-level cron job triggers `wp-cron.php`.
- Filesystem Credentials: If WordPress requires FTP/SSH credentials for file operations, these must be correctly defined for WP Optimal State’s file-based features (settings, logs, backups) to work. Define in `wp-config.php` or allow WordPress to prompt. `define(‘FS_METHOD’, ‘direct’);` might be needed on some server setups but requires correct file ownership/permissions.
Database Server Configuration (`my.cnf` / `my.ini`)
Server tuning affects overall performance:
- `innodb_buffer_pool_size`: Crucial for InnoDB performance.
- `max_allowed_packet`: Can affect large data imports/exports.
- `query_cache_size` (Older MySQL): Can impact query performance.
- `tmp_table_size`, `max_heap_table_size`: Affect complex query performance.
Consult your hosting provider or a database administrator for server tuning.
Support
Getting Help
Self-Help Resources
- This Manual: Review relevant sections for features, troubleshooting, and FAQs.
- X Profile: lukegarri
- Support Form: https://payhip.com/optistate/contact
- Plugin page on WordPress.org: https://wordpress.org/plugins/optistate/
Before Requesting Direct Support
Please gather the following information:
- Environment Details: WordPress version, PHP version, MySQL/MariaDB version, Hosting provider.
- Plugin Version: WP Optimal State version number (currently 1.3.1).
- Issue Description: Clearly describe the problem, including:
- What action were you performing?
- What did you expect to happen?
- What actually happened?
- Exact error messages (copy and paste).
- Steps to reproduce the issue consistently.
- Troubleshooting Steps Already Taken: Mention if you tried solutions from this manual (e.g., conflict testing, enabling debug mode, checking logs).
- Relevant Logs/Screenshots: Provide snippets from `debug.log` (if WP_DEBUG was enabled) or screenshots of the error/issue if helpful.
Enabling WP_DEBUG (`wp-config.php`) can often provide crucial error details.
Reporting Bugs
If you believe you’ve found a bug:
- Confirm It’s the Plugin: Temporarily deactivate other plugins and switch to a default theme to rule out conflicts.
- Check for Updates: Ensure you are using the latest version of WP Optimal State.
- Gather Information: Collect all details listed in “Before Requesting Support”.
- Submit Report: Use the contact methods provided (e.g., support form, official plugin pages) and provide clear, reproducible steps and environment details.
Feature Requests
Suggestions for improvements or new features are welcome:
- Explain the Need: Describe the problem you’re trying to solve or the functionality you’d like to see.
- Suggest Implementation (Optional): If you have ideas on how it could work.
- Submit Request: Use the provided contact methods.
Contributing
- Translations: Help translate the plugin into other languages using the provided `.pot` file and standard translation tools (like Poedit or Loco Translate).
- Testing: Test the plugin in different environments (PHP versions, hosting) and report any issues found.
- Feedback: Provide constructive feedback on usability and features.
- Code Contributions (Advanced): Contact the developer if you wish to contribute code patches or improvements, following WordPress coding standards.
Privacy & Data Collection
WP Optimal State is designed with privacy in mind:
- ✅ Operates entirely within your WordPress installation.
- ✅ Does NOT send any database contents, statistics, settings, or user data to external servers.
- ✅ Does NOT use external APIs for its core functionality (except potentially for translation updates via WordPress mechanisms).
- ✅ Does NOT track user activity within the plugin for analytics purposes.
- ✅ Stores settings and logs locally on your server (`wp-content/uploads/optistate-settings/`).
Your site data remains on your server.
License Information
License: GNU General Public License v2.0 or later (as declared in `optistate.php`)
License URI: https://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl-2.0.html
This means the plugin is free software. You are free to use, modify, and redistribute it under the terms of the GPLv2 or later version. Any modifications or derivative works must also be licensed under the GPL.
Appendix
Glossary of Terms
- AJAX (Asynchronous JavaScript and XML): Technology used by the plugin for background communication (e.g., running cleanups without full page reload).
- Atomic Swap: The database restore technique using `RENAME TABLE` within a transaction to switch tables instantly and safely.
- Auto-draft: Automatically saved post draft created by WordPress during editing.
- Autoload: WordPress options (`wp_options` table) loaded automatically on every page load.
- Checksum: A digital fingerprint (e.g., SHA-256 hash) used to verify file integrity.
- Cron (WP Cron): WordPress’s system for scheduling tasks (like automated cleanups).
- CSRF (Cross-Site Request Forgery): A type of web security vulnerability nonces help prevent.
- Database Optimization: Improving database performance by reorganizing data, updating statistics, and reclaiming space.
- Database Repair: Fixing structural corruption or errors within database tables.
- Fragmentatio / Overhead (`data_free`): Unused space within a database table file resulting from deletions/updates.
- InnoDB / MyISAM: Common storage engines used by MySQL/MariaDB tables, affecting features and performance.
- Metadata (Post Meta, Comment Meta, User Meta): Additional key-value data associated with posts, comments, or users.
- Nonce (Number used once): Security token used by WordPress to verify the intent of actions.
- Orphaned Data: Database entries (e.g., metadata, relationships) that refer to parent items (e.g., posts, comments) that no longer exist.
- phpMyAdmin: Common web-based tool for managing MySQL/MariaDB databases.
- Revision: A saved version of a post or page created during editing.
- Staging Site: A copy of a live website used for testing changes before deploying them.
- Transient: Temporary cached data stored in the `wp_options` table with a set expiration time.
- WP-CLI (WordPress Command Line Interface): A tool for managing WordPress sites via commands in a terminal.
- XSS (Cross-Site Scripting): A type of web security vulnerability output escaping helps prevent.
Useful SQL Queries (Run via phpMyAdmin or similar tools)
⚠️ Warning: Execute direct SQL queries with extreme caution. Always back up your database first. Replace `wp_` with your actual table prefix if different.
-- Check total database size
SELECT table_schema "Database Name",
ROUND(SUM(data_length + index_length) / 1024 / 1024, 2) "Size (MB)"
FROM information_schema.TABLES
WHERE table_schema = DATABASE() -- Use DATABASE() for current DB
GROUP BY table_schema;
-- Find 10 largest tables by size (Data + Index)
SELECT table_name "Table Name",
ROUND(((data_length + index_length) / 1024 / 1024), 2) "Size (MB)"
FROM information_schema.TABLES
WHERE table_schema = DATABASE()
ORDER BY (data_length + index_length) DESC
LIMIT 10;
-- List tables with significant overhead (fragmentation)
SELECT table_name "Table Name",
ROUND(data_free / 1024 / 1024, 2) "Overhead (MB)"
FROM information_schema.TABLES
WHERE table_schema = DATABASE()
AND data_free > 1024 * 1024 -- Show tables with > 1MB overhead
ORDER BY data_free DESC;
-- Count rows in each table
SELECT table_name "Table Name", table_rows "Row Count"
FROM information_schema.TABLES
WHERE table_schema = DATABASE()
ORDER BY table_rows DESC;
-- Find 10 largest autoloaded options by data length
SELECT option_name, LENGTH(option_value) AS value_size
FROM `wp_options`
WHERE autoload = 'yes'
ORDER BY value_size DESC
LIMIT 10;
-- Calculate total size of autoloaded options
SELECT ROUND(SUM(LENGTH(option_value)) / 1024, 2) AS "Total Autoload Size (KB)"
FROM `wp_options` WHERE autoload='yes';
-- Count post revisions per post
SELECT post_title, COUNT(*) AS revision_count
FROM `wp_posts`
WHERE post_type = 'revision'
GROUP BY post_parent
ORDER BY revision_count DESC
LIMIT 10;
-- Count different comment types
SELECT comment_type, COUNT(*) AS count
FROM `wp_comments`
GROUP BY comment_type;
Resources
Official WordPress Resources
- WordPress.org
- WordPress Developer Resources (Code Reference)
- WordPress Support Forums
- WordPress Documentation
Database Optimization & Management
- MySQL OPTIMIZE TABLE Syntax
- MariaDB OPTIMIZE TABLE Syntax
- WordPress Database API Handbook
- Database Optimization Guides (e.g., Kinsta Blog)
Performance Testing Tools
Backup Solutions (Alternatives/Complements)
- UpdraftPlus
- BackWPup
- Duplicator
- Your Hosting Provider’s Backup Service
Version History
Version 1.3.1 (Current) – March 2026
- Updated the server-side caching feature to improve the performance and reliability of the cache preloading and cache purging functionalities.
- Improved the reliability of the Legacy Plugin Data Scanner to minimize false positives.
- Added two performance features: Removal of 1. Feed Links (RSS & Atom) and 2. Post Relational Links.
- Powered up the Database Query Caching feature by adding two extra settings and optimizing how things work.
- Added validation of security headers via external link to the Browser Caching feature.
- Added several new recommendations to the Health Score Database tool.
- Added several new recommendations to the Performance Metrics (PageSpeed) tool.
- Implemented an additional security check in the database table deletion function within the Database Structure Analysis tool.
- Refined the Login Page Protection tool to increase its efficiency and reduce its impact on website performance.
- Completely redesigned the main plugin class (class-optistate.php), optimizing a dozen areas for greater efficiency and improved compatibility.
Version 1.2.3 – Feb. 2026
- The JavaScript code has been completely rewritten for better efficiency and reliability.
- Improved Legacy Plugin Data Scanner for deeper scanning.
- Expanded the database of plugins and themes detected by Legacy Plugin Data Scanner.
- Improved the scan depth of the Database Search & Replace functionality.
- Fixed a bug in the database statistics retrieval that caused an error when refreshing.
- Optimized the integration of Performance Metrics (PageSpeed) for faster and more accurate reporting.
- Expanded the capabilities of the Database Structure Analysis tool, which now displays plugin/theme names alongside their corresponding database table
- names.The Bad Bot Blocker tool has been upgraded and now works perfectly and efficiently on Nginx servers as well.
- The Login Page Protection tool has been revised to increase its efficiency against massive brute force attacks, while still being completely reliable.
- The user manual has been updated, expanded, and is now more user-friendly.
Version 1.2.2 – Feb. 2026
1. New Feature: Legacy Plugin Data Scanner:
- Detects data left behind by plugins/themes you have uninstalled
- Includes accurate security measures to avoid false positives
- The most powerful and comprehensive tool available in this category
2. Refined the database restore system:
- Full disabling on WordPress Multisite
- Enhanced the efficiency of several functions
- Increased protection against SQL injection
- Added how-to instructions in case of a stuck restore process
- Compatibility with phpMyAdmin exports increased to 100%
- Optimized server resource management to minimize errors and crashes
3. Refinements to the login page protection against brute force attacks, minimizing memory and CPU waste during massive attacks.
4. Improved the security and behavior of several cleanup operations related to WooCommerce and duplicate post meta/comment meta.
5. Enhanced the accuracy of statistics and the efficiency of database queries related to retrieving such statistics.
6. Added a new performance feature: Font Loading Optimization.
7. Improved both the efficiency and reliability of the Bad Bot Blocker on Nginx servers.
8. Expanded the user manual by including new sections and updating existing ones to be more user-friendly.
Version 1.2.1 – Jan. 2026
- Critical Fix: Database restore now works correctly with phpMyAdmin exports. We fixed an error that prevented restores from completing (the dreaded “Multiple primary key defined” message).
- Code Cleanup: Reorganized the plugin’s internal code by splitting a massive 318-method file into 8 smaller, focused components. Think of it like organizing a cluttered garage into labeled sections.
- Better Tools: Created a new utilities toolkit that makes backup and restore operations more reliable and easier to maintain going forward.
- Security: No security downgrades—everything that was protected before is still protected. We even added extra validation to prevent SQL injection during restores.
- Faster & Lighter: Small but measurable improvements—the plugin uses 2-5% less memory and runs 1-3% faster thanks to the reorganization.
- For Developers: If you’ve written custom code that references OPTISTATE::LOGIN_TABLE_NAME, you’ll need to update it to OPTISTATE_Login_Protection::TABLE_NAME. Regular users aren’t affected.
- Smooth Upgrade: Your existing backups will still work perfectly. The plugin maintains full backward compatibility, so upgrading is painless.
- Bottom Line: Update immediately—this version fixes a critical issue while making the plugin more efficient and maintainable for the future.
Version 1.2.0 – Jan. 2026
- Smart Polling Intervals: Updated admin.js to dynamically adjust the polling interval in pollRestoreStatus based on the server’s response time, reducing admin-ajax.php load during long restores.
- Resilient Rate Limiting: Improved check_rate_limit to handle rapid concurrent requests more gracefully by utilizing set_transient with a shorter expiration buffer.
- Database Size Caching: Modified get_total_database_size to force a cache refresh ($force_refresh = true) immediately after a “One-Click Optimization” to ensure the dashboard reflects accurate gains.
- Memory Management: Enhanced _backup_table_data_chunked to call gc_collect_cycles() more frequently during the export of large tables like wp_posts, preventing memory exhaustion errors.
- Regex Pattern Caching: Cached the compilation of exclude patterns in get_compiled_exclude_patterns to a static property, improving page load performance when “Server-Side Caching” is enabled.
- Fixed: Addressed an issue in clean_orphaned_postmeta where the DELETE query could time out on extremely large databases by implementing stricter LIMIT batching.
- Fixed: Corrected a logic error in is_safe_restore_query that occasionally flagged valid INSERT statements containing the word “DROP” within the content string as security risks.
- Fixed: get_trusted_host now correctly sanitizes the HTTP_HOST header to prevent potential cache poisoning when generating cache file paths.
- Fixed: Ensured restore_backup properly resets the optistate_maintenance_mode_active option if a fatal error occurs during the restoration process.
- Code Hardening: Applied stricter sanitize_text_field input validation in ajax_save_auto_settings to prevent non-numeric values from being saved for auto_optimize_days.
Version 1.1.7 – Dec. 2025
- New feature: Database search & replace. Ideal for updating the database after a migration.
- New user interface split into separate tabs for a smooth and easy browsing experience.
- In the Database Structure Analysis, added an option to delete database tables that haven’t been used for over a month.
- Added four additional cleanup options (Action Scheduler, Embed Cache, WooCommerce Cleanup, Unused Terms).
- Added new descriptions and recommendations to the admin interface to improve user experience.
- Expanded and updated the user manual, added an advanced search functionality and other minor improvements.
Version 1.1.6 – Nov. 2025
- Database restore process has been refined for greater efficiency, with restore times reduced by 20–30%.
- Database file upload (for the restore process) has been revised and improved to avoid server timeouts during very large upload sessions.
Version 1.1.5 – Nov. 2025
- Expanded the Activity Logs to include more events.
- Strengthened the rate limiting system by implementing it both client-side and server-side.
- Improved the efficiency of all functions concerning database statistics fetching.
- Added a new check on files uploaded via the database restore function to ensure that these files do not contain potentially harmful SQL code.
- Improved the efficiency of the function responsible for purging the cache (server-side caching).
- Improved the efficiency of checksum generation system for database backups.
- Improved the reliability of the database recovery process in case of server error.
- Revised server caching functionality for faster page loading and lower Time to First Byte (TTFB).
Version 1.1.4 – Nov. 2025
- New feature: Settings Export & Import.
- Added instructions for Nginx users to enable directory protection not based on .htaccess files.
- Expanded .htaccess caching rules for the Browser Caching feature.
- Perfected both the database backup and the restore functions by adjusting and enhancing some critical parameters and variables.
- Safety rollback process revised for greater reliability and a higher success rate.
- Upgraded ‘Restore from File’ functionality to accept files as large as 1GB (previously 500 MB).
- Improved UI with more details and better explanations.
- Updated the user manual to reflect these updates.
- Updated the uninstall file for complete removal of all transients, folders, and data generated by the plugin.
Version 1.1.3 – Nov. 2025
- New Feature: Automatic Cache Preloading. Rebuild your entire website cache with a single click. This feature detects your sitemap and visits every single URL in it, ensuring that your visitors benefit from maximum loading speed from the very first visit.
- Smart Mobile Detection: A new, efficient mobile detection function (detect_mobile()) has been added. The result is cached for the duration of the request to ensure minimal performance impact.
- Cache Race Condition Fix: Implemented an atomic file locking system to prevent cache file corruption that could occur under high traffic.
- Cache Directory Hardening: The page-cache directory security has been upgraded to block all direct file access, except for the necessary .html cache files. This prevents script execution and protects system files.
- Performance: The cache preload function has been refined to be faster and more reliable, particularly for sites with thousands of pages/posts.
- Fixed a bug in custom consent cookie processing.
- Updated the uninstall file for complete removal of all transients, folders, and data generated by the plugin.
- Minor code optimizations to ensure consistently stable and reliable functioning.
Version 1.1.2 – Nov. 2025
- New Feature: Server-Side Page Caching. Simple and effective with minimal setup.
- Improved the emoji scripts deactivation feature.
- Optimized some unnecessary and redundant code.
- Extended the usage of Wp_Filesystem to all functions that can benefit from it.
- Removed some functions that were no longer necessary after merging them into broader ones.
- Enhanced the security of browser caching feature concerning .htaccess file handling.
- Added a preventive check to the feature to set the limit for post revisions, in case this limit is already included in the WP configuration file.
- Strengthened the database recovery mechanism with respect to swap_temp_tables_to_live() function.
- Implemented an additional safety mechanism in the database restore process based on a second automatic attempt 10 seconds after the first failure.
- Added a close button to toast messages.
- Fixed the readme file according to WordPress formatting standards.
Version 1.1.1 – Oct. 2025
- New Feature: Performance Features Manager. Granular control over WordPress core features like Heartbeat API, Post Revisions, Emoji Scripts, XML-RPC, Self Pingbacks, and various header meta tags/links (REST API, Shortlink, RSD, WLW Manifest, WP Version). Allows disabling unused features for potential performance and security gains.
- New Feature: Browser Caching via .htaccess (under Performance Manager).
- Bug Fix: Corrected an issue where the .htaccess caching rules were not fully removed upon browser caching deactivation, ensuring the entire code block (including all wrapping comment lines) is now securely deleted.
- Improvement: Database Restore Engine. Optimized the core restore logic (`_perform_restore_core`) for better handling of large files, improved memory management during SQL execution, added batch processing with transactions, and refined temporary table swapping (`swap_temp_tables_to_live`) with enhanced error handling and rollback mechanisms.
- Improvement: Restore from File Compatibility. Enhanced validation (`validate_sql_file_simple`) for uploaded SQL files to better support standard exports (e.g., from phpMyAdmin) by checking for core tables and database name comments, while retaining security checks.
- Improvement: Logging & Debugging. Refined logging for scheduled tasks, backup/restore operations (`log_restore_operation`, `log_failed_restore_operation`), and email notifications. Added more detailed error logging for filesystem and database issues.
- Bug Fix: File System Initialization. Improved robustness of WP_Filesystem initialization and checks throughout the plugin.
- Bug Fix: Cron Scheduling. Corrected potential issues with scheduling and rescheduling automated tasks (`update_cron_schedule`, `maybe_reschedule_cron`).
- UI/UX: Added collapsible section for Performance Features Manager. Minor styling adjustments in `admin.css`.
- Security: Added checksum verification before backup downloads (`handle_download_backup`). Strengthened path validation in multiple areas. Added content sniffing for uploaded restore files.
Version 1.1.0 – Oct. 2025
- UI Polish: General styling improvements.
- New Function: Database Structure Analysis.
- Security Hardening: SQL injection protection (`validate_table_name`), file path traversal prevention (`validate_file_path`).
- Improvement: Timeout Prevention (`set_backup_limits`, `set_optimization_limits`).
- Improvement: Transactional Restore Rollback System with Safety Backup.
- Improvement: Client-Side Upload Validation (Type & Size).
Version 1.0.9 – Oct. 2025
- New Function: Restore Database from File (Initial version).
- Bug Fix: Backup creation failure after lowering max backups limit.
- Improvement: Updated uninstaller script.
- Improvement: Enhanced email notification reliability.
Version 1.0.8 – Sept. 2025
- New Feature: Email Notifications for scheduled tasks.
- New Feature: Backup Verification (Checksum & Metadata).
- Improvement: Smart Rollback for failed restores.
- Improvement: Timeout Protection for restores.
- Improvement: Secure Atomic File Writes.
- Improvement: Better Error Handling & Messages.
Version 1.0.7 – Sept. 2025
- New Setting: Customizable maximum backups limit.
- Improvement: Enhanced optimization history logs.
- Bug Fix: Transient expiration logic for rate limiting.
- Added: Database creation date to statistics.
Version 1.0.6 – Aug. 2025
- Security Fix: Addressed potential SQL injection vectors.
- Security Improvement: Enhanced file download security.
- Improvement: Memory management for large DB operations.
- Improvement: Backup batch processing.
- Improvement: Automatic backup directory protection.
- Improvement: Error handling for rate limits.
Version 1.0.5 – July. 2025
- New Feature: Automated Cleaning Scheduler.
- Improvement: Database restoration process reliability.
- UI Redesign: Improved clarity and usability.
- Added: Automatic backup before scheduled cleanup.
- Improvement: Enhanced activity logging.
- Improvement: Better status indicators.
Version 1.0.4 – June 2025
- New Feature: Integrated Database Backup Manager (Create, Restore, Download, Delete).
- Improvement: Table analysis/repair script enhancements.
- UI/UX: Added confirmation modals and toast notifications.
- Compatibility: Updates for WordPress 6.9.
- Minor bug fixes and performance tweaks.
Version 1.0.3 – May 2025
- New Feature: Analyze & Repair Tables.
- UI Redesign.
- Security: SQL injection hardening, settings sanitization.
- Improvement: Error handling, code structure.
- Compatibility: Updates for WordPress 6.8.
Version 1.0.2 – Feb. 2025
- Added: Internationalization support (`.pot` file).
- Security: Enhanced escaping and sanitization.
- Improvement: SQL query preparation.
- Compatibility: Updates for WordPress 6.7.
- Documentation improvements.
Version 1.0.1 – Jan. 2024
- Initial public release.
- Feature: One-click optimization.
- UI improvements.
- Feature: Autoload optimization.
- Feature: Enhanced statistics display.
Version 1.0.0 – Nov. 2024
- Initial development release.
- Core cleanup functionality (revisions, spam, transients, orphans).
- Database table optimization (`OPTIMIZE TABLE`).
- Basic statistics display.
Credits
Developed By: Luke Garrison 🔗 – The Spiritual Seek
X Profile: lukegarri
Github: lukegarrisondev
Website: spiritualseek.com
Plugin URI: spiritualseek.com/wp-optimal-state-wordpress-plugin/
License: GPL v2 or later
Built With:
- WordPress Core APIs (`$wpdb`, WP_Filesystem, Options API, Cron API, AJAX API, etc.)
- PHP
- MySQL / MariaDB SQL commands
- jQuery (Bundled with WordPress)
- CSS3
Special Thanks: WordPress community, beta testers, users providing feedback.
Contact Information & Support
Plugin Support: Please use the contact methods provided below.
X Profile: lukegarri
Support Form: https://payhip.com/optistate/contact
Conclusion
Thank you for using WP Optimal State! We hope this plugin helps you maintain a clean, efficient, and fast WordPress database. By leveraging its features—from detailed cleanups and optimizations to safe backups/restores and performance tweaks—and following the safety guidelines, you can ensure your site runs smoothly.
Key Takeaways
- Backup First, Always: Before any significant operation.
- Use Automation Wisely: The scheduler is great for routine maintenance.
- Understand Actions: Know what each cleanup and performance feature does.
- Monitor Health: Use statistics and health score to guide maintenance.
- Combine Efforts: Use WP Optimal State alongside caching, image optimization, and good hosting.
Getting the Most from WP Optimal State
- Establish a maintenance schedule (automated or manual).
- Regularly review statistics and health score.
- Periodically test backup restoration on a staging site.
- Explore the Performance Features Manager to tailor WordPress core functions.
- Keep the plugin, WordPress, and PHP updated.
Happy Optimizing!
User Feedback
“Finally, a real speed difference!” – by Mark WebDev
I’ve been running a content-heavy blog for 5 years and my database had ballooned to over 1 GB. After using the One-Click Optimization feature, I immediately saw a 35% reduction in database size and my admin dashboard loads noticeably faster – what used to take 4-5 seconds now loads in under 2.5 seconds. The cleaning power is genuinely impressive. Highly recommend running this weekly!
“Powerful and advanced plugin” – by Larry
I give it 4 stars instead of 5 because the free version does not allow me to restore the database via upload. For a control freak like me, this is a limitation, because I immediately download backups after creating them, since leaving them online is not 100% secure anyway.
“The automated backup mention saved me” – by Digital Sarah
I love that the documentation is crystal clear about creating backups BEFORE cleaning. I followed the instructions, ran a full cleanup on my messy WooCommerce site, and everything went smoothly. Removed over 2,500 post revisions I didn’t even know existed. The fact that they emphasize safety first shows they actually care about users not breaking their sites.
“Autoloaded options optimization is a game-changer” – by TechGuru_James
The autoloaded options optimizer is incredibly useful! I had no idea some plugins were loading 300KB+ of data on EVERY page request. This feature identified the culprits and optimized them automatically while protecting critical settings. My site’s memory usage dropped significantly and pages load about 150ms faster. This alone makes the plugin worth it.
“Simple interface, powerful results” – by Blogger Bella
I’m not a technical person, but this plugin makes database maintenance so easy. The color-coded buttons and clear warnings help me understand what’s safe to clean. I run the weekly One-Click Optimization every Sunday evening and it takes literally 30 seconds. My site feels snappier and my hosting costs went down because my backups are smaller now!
“Cleared 7,000+ spam comments effortlessly” – by Rick
My forum had accumulated 47,000+ spam comments over the years (even with Akismet). This plugin cleaned them all in under a minute. The statistics dashboard is brilliant – seeing exactly how many orphaned entries, expired transients, and trashed items exist helps me understand what’s bloating the database. Clean interface, powerful engine.
“Great for client sites maintenance” – by Lisa V.
We manage 30+ client websites and WP Optimal State 1.0.3 has become part of our monthly maintenance routine. The manual is exceptionally detailed which makes training new team members easy. Only complaint is there’s no automatic scheduling yet, but the developer mentioned it might come in future updates. Still, manually running it monthly takes minimal time.
“Recovered 1.2GB of database space!” – by EcommerceSteve
My WooCommerce store had 8+ years of accumulated junk. After running a full cleanup with this plugin, I recovered 1.2GB of database space – that’s a 42% reduction! The transient cleanup alone removed thousands of expired cache entries. Database queries are faster, checkout is smoother, and my hosting provider even noticed the improved performance. Worth every minute spent reading the manual first.
“The revision cleanup saved my site” – by Mike The Writer
As a daily blogger, I had over 12,000 post revisions eating up database space and slowing everything down. The old revisions cleanup feature with customizable age limits is perfect – I set it to keep revisions from the last 30 days and nuked everything older. My database shrunk by 28% and admin editing is noticeably more responsive. Such a relief!
“Best free optimization plugin I’ve found” – by Amanda Jordan
I’ve tested dozens of database optimization plugins and this is the most comprehensive free option available. The fact that it identifies and optimizes large autoloaded options automatically sets it apart. The security features are solid (nonce verification, capability checks, SQL injection prevention) and it doesn’t collect any user data. Clean code, respects WordPress standards, and actually works.
“The troubleshooting guide is great” – by Carlos Burren
I encountered a timeout error on my first cleanup attempt (huge database, shared hosting), but the troubleshooting section in the manual had the exact solution. Increased my PHP timeout settings and everything worked perfectly. The comprehensive documentation shows they actually thought through real-world scenarios. Cleaned 23,000 orphaned postmeta entries and optimized all tables without breaking anything. Professional quality plugin.
Send your feedback to: lukegarrison.dev@gmail.com
